| Journal of Medical Cases, ISSN 1923-4155 print, 1923-4163 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Med Cases and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.journalmc.org |
Case Report
Volume 12, Number 5, May 2021, pages 186-189
Subcapsular Hepatic Hematoma Post-Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Requiring Surgical Necrosectomy
Ryan Petruccia, b, Amitabha Dasa
aDepartment of UGI Surgery, Liverpool Hospital, Sydney, NSW 2170, Australia
bCorresponding Author: Ryan Petrucci, Department of UGI Surgery, Liverpool Hospital, Sydney, NSW 2170, Australia
Manuscript submitted February 1, 2021, accepted February 15, 2021, published online March 5, 2021
Short title: Subcapsular Hepatic Hematoma Post-ERCP
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/jmc3672
| Abstract | ▴Top |
Cholelithiasis is a common gastrointestinal pathology with a prevalence of over 6% in the USA. Symptomatic patients can develop cholangitis, biliary colic, pancreatitis and cholecystitis. Surgical management involves laparoscopic or open cholecystectomy. Stones within the common bile duct can be treated with endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP). Well-known ERCP complications include pancreatitis, perforation, bleeding and cholangitis. Hepatic hematomas as a complication of ERCP are extremely rare, with fewer than 50 reported cases in the literature. Approximately 22% have required operative management. We present an extremely rare case of ERCP-associated subcapsular hepatic hematoma in a 43-year-old lady that was initially non-operatively managed. She did not improve with antibiotics alone and underwent attempted interventional radiology drainage. Despite this, due to on-going sepsis, the patient underwent laparoscopic necrosectomy and drain placement with continued post-operative irrigation. After a long course of antibiotics and drain irrigation, the patient was discharged with repeated computed tomography imaging showing almost total resolution of the infected collection. This case highlights the extreme rarity of surgical management for post-ERCP subcapsular hepatic hematoma and its successful outcome.
Keywords: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography complications; Hepatic hematoma; Liver hematoma; Subcapsular hepatic hematoma
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Cholelithiasis is a relatively common medical condition and has an estimated prevalence in the USA of 6% and 9% in men and women, respectively [1]. There is also geographical and ethnic diversity with Caucasians more commonly affected compared to Afro-Caribbean populations [2]. Whilst the vast majority of patients with cholelithiasis are asymptomatic, associated pathology includes biliary colic, cholecystitis, gallstone pancreatitis and cholangitis [3]. Several of these complications require treatment via surgical and endoscopic interventions.
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) has developed into a widely used procedure to investigate and manage biliary and pancreatic pathologies.
ERCP complications have a reported incidence of 2.5-8% and include pancreatitis, bleeding from sphincterotomy, cholangitis and perforation [4-6]. Subcapsular hepatic hematoma is an exceeding rare complication. A recently published literature review for subcapsular hepatic hematomas secondary to ERCP demonstrated fewer than 55 published cases [7]. Of relevance to this unusual case, the requirement for surgical intervention is even scarcer with previous reviews demonstrating surgical management in less than one-third of cases [7-9].
| Case Report | ▴Top |
An otherwise healthy 43-year-old lady was admitted to our hospital with right upper quadrant (RUQ) pain, fevers and vomiting. Her blood tests revealed raised inflammatory markers and a raised bilirubin of 87 µmol/L (reference range < 20 µmol/L). She was admitted under the gastroenterologists and treated for ascending cholangitis with intravenous (IV) antibiotics. Abdominal ultrasound demonstrated cholelithiasis and choledocholithiasis without signs of cholecystitis.
On day 1 of her admission, she underwent an ERCP. Her common bile duct (CBD) was cannulated with a guidewire and her CBD was swept via balloon with multiple stones extracted. A sphincterotomy was performed and a CBD stent was placed in an acceptable position and bile flowed freely through the stent. The ERCP recovery was uneventful and after convalescence with antibiotics, the patient was referred to the general surgeons. One week after ERCP, she proceeded to have a laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Surgery was uneventful and upon discharge she was booked to have a repeat ERCP and removal of CBD stents under the gastroenterology team. Unfortunately due to the coronavirus pandemic, her appointment was postponed by several months.
After 5 months, the patient was admitted for elective ERCP with stent removal. During the procedure, her CBD stent was removed, a guidewire was again passed in to the biliary tree and a balloon sweep was undertaken, which removed further CBD stones. Post-procedure in the recovery department, the patient complained of right shoulder tip pain and worsening RUQ pain. This settled with analgesia and she was discharged home from the endoscopy suite. She re-presented the following day with severe RUQ pain and was found to be tachycardic. Computed tomography (CT) of her abdomen and pelvis with oral and IV contrast showed a large subcapsular hepatic hematoma affecting most of the right liver lobe with some mass effect on the inferior vena cava (Figs. 1, 2).
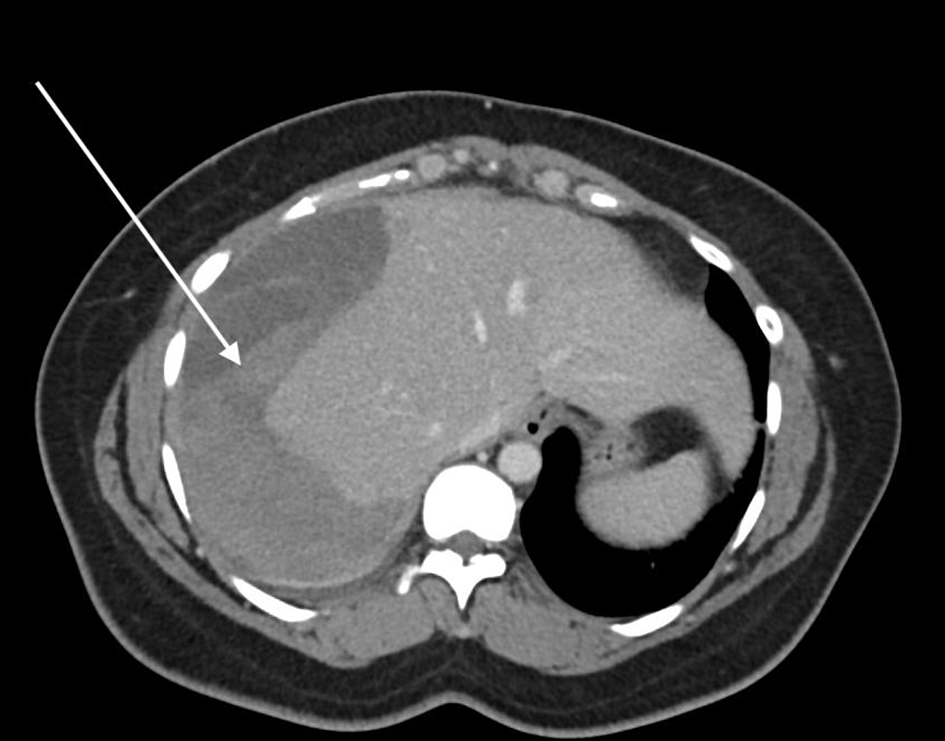 Click for large image | Figure 1. Axial CT demonstrating the large subcapsular hepatic hematoma involving most of the right lobe of the liver, highlighted by the arrow. CT: computed tomography. |
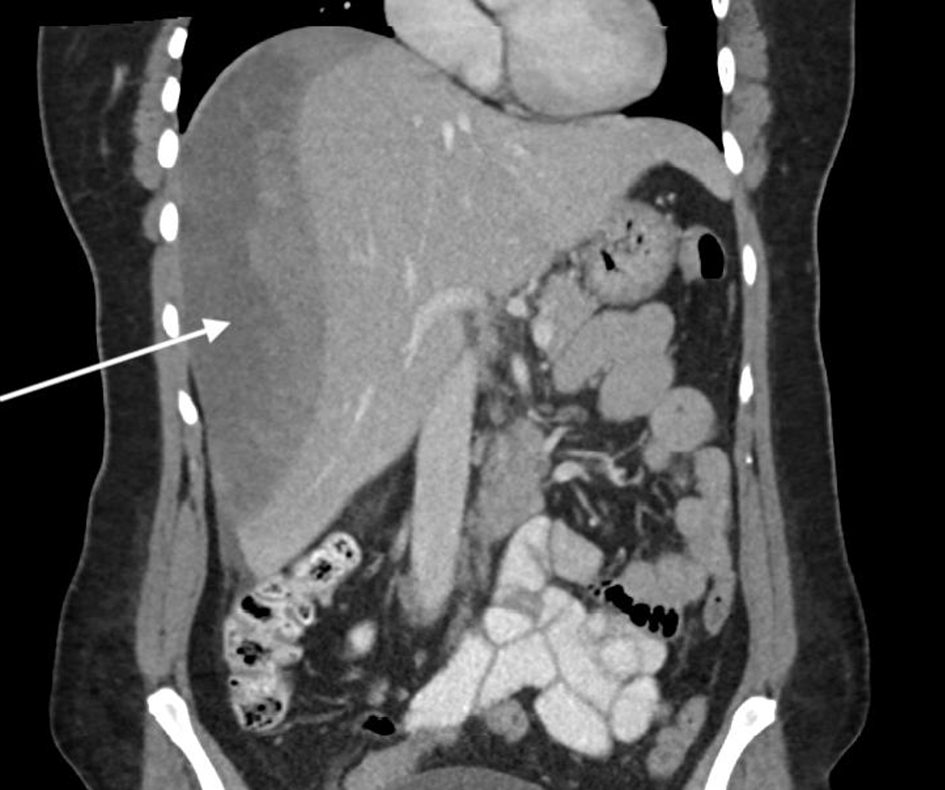 Click for large image | Figure 2. Coronal CT of abdomen showing the large hematoma, highlighted by the arrow. CT: computed tomography. |
The general surgery team on call were consulted and advised continued close observation, repeat hemoglobin testing and non-operative management. Progress CT scans showed a stable subcapsular hematoma without peritoneal extension. The patient’s pain improved and after remaining stable she was discharged on day 7 of the admission. Five days later, she re-presented to emergency department with a return of RUQ pain. Additionally, she also complained of shortness of breath, new fevers, malaise and lethargy. On assessment, she showed signs of sepsis and had a new oxygen requirement. Repeat CT imaging showed the continued presence of the large subcapsular hepatic hematoma and a new right-sided small pleural effusion.
She was admitted under the gastroenterology team and required admission to the intensive care department for on-going hemodynamic support. The patient was treated for an infected subcapsular hematoma and underwent interventional radiology (IR) guided drainage of the collection. Unfortunately, the drain did not facilitate resolution of the collection and the patient did not improve from a sepsis point of view.
The upper gastrointestinal (UGI) surgery team was consulted and after discussion with the treating gastroenterology team, the patient underwent laparoscopic washout of the infected collection. It was reported that the right lobe of the liver was densely adherent to the right hemidiaphragm with a necrotic capsule present. This was partially de-roofed and drainage of purulent liquid, necrotic debris and old blood was suctioned. Despite the laparoscopic washout, the patient required a further take back to theater 7 days later due to on-going fevers, raised inflammatory markers and a repeat CT which showed an on-going septated subcapsular collection. The surgical approach for the second operation included a partial necrosectomy of the collection and liver capsule and the cavity was thoroughly irrigated. No bile leak was seen and intra-operatively it was decided to leave a large caliber silicone double lumen sump drain in situ in the cavity, and to have continued irrigation of the sump drain post-operatively. In addition to the sump drain, two 28f Blake® drains were placed and kept in situ for several days.
Continued irrigation and drainage of the sump tube with normal saline was performed for 7 days. In addition to this, the patient had 40 days of IV antibiotics after Klebsiella oxytoca and Escherichia coli growth from the collection. This management was successful and the patient did not require any further surgical interventions. Continued monitoring of the drain output did not show any evidence of a bile leak during her recovery. Progress CT imaging several weeks after surgical intervention demonstrated significant reduction of the collection (Figs. 3, 4).
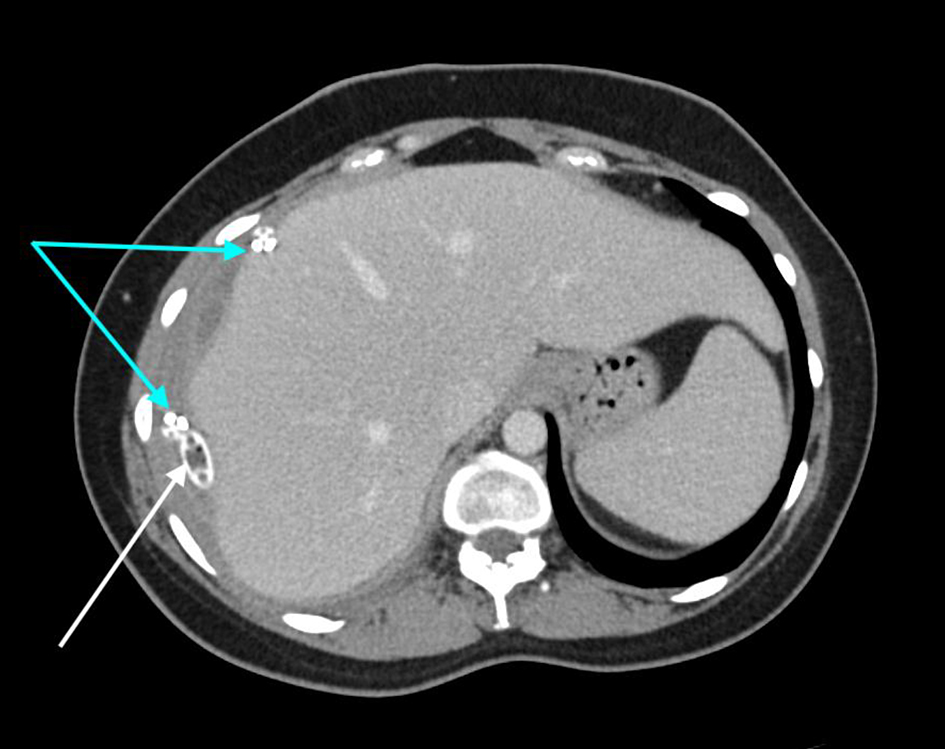 Click for large image | Figure 3. Axial CT demonstrating the interval reduction in size of subcapsular collection. The white arrow highlights the sump drain and the blue arrows show the Blake® drains. CT: computed tomography. |
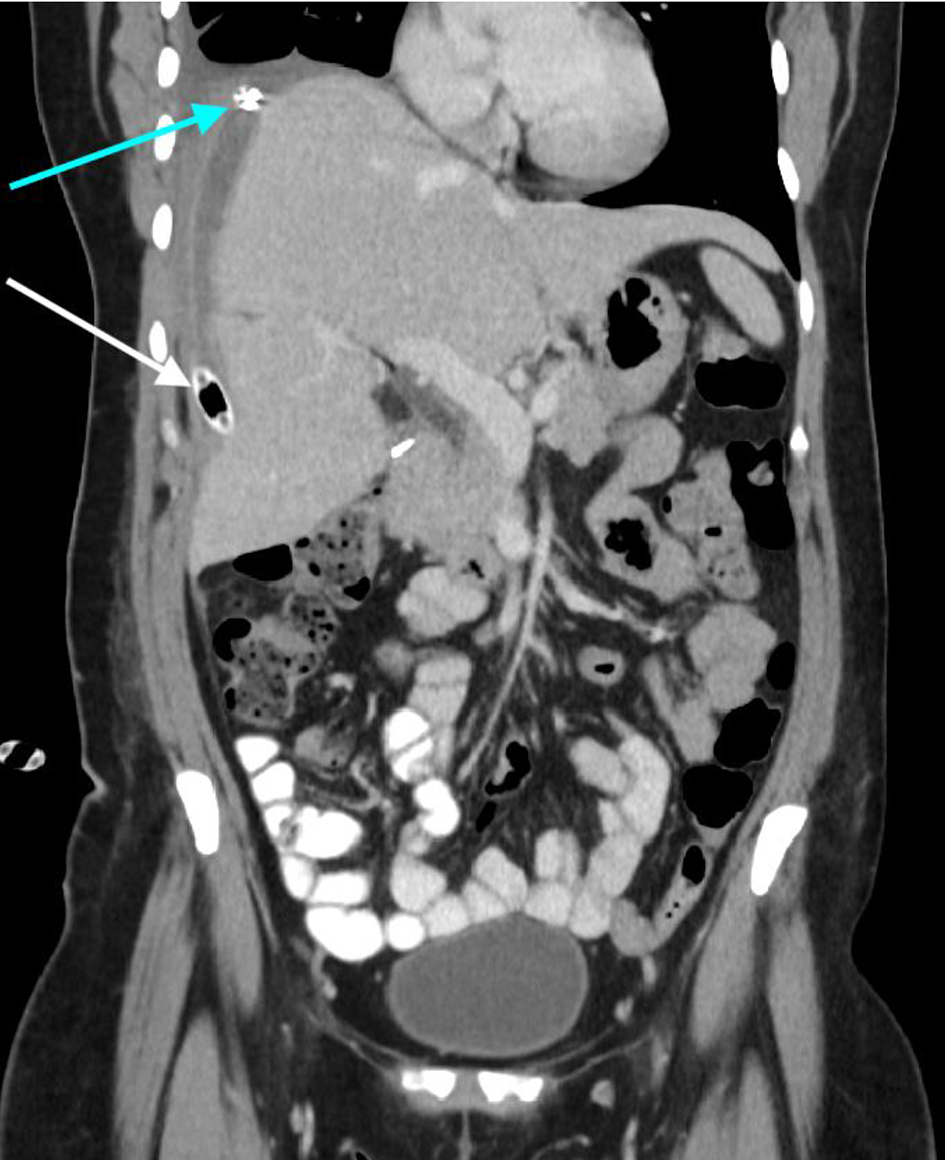 Click for large image | Figure 4. Coronal CT illustrating the interval significant decrease in the size of collection. The white arrow highlights the sump drain in position and the blue arrow demonstrates the Blake® drain. CT: computed tomography. |
An additional morbidity the patient suffered from during her inpatient admission was an acute kidney injury (AKI) due to antibiotic toxicity. This occurred due to a supratherapeutic antibiotic level causing a direct acute tubular necrosis. After the patient’s AKI resolved, she was discharged with her sump drain in situ and seen regularly by community nurses. She was reviewed regularly in outpatient clinic after discharge and the drain was systematically partially removed and shortened in size until eventually being completely removed without issue. She has been reviewed since drain removal and does not demonstrate any long-term complications from the admission.
| Discussion | ▴Top |
Subcapsular hepatic hematomas are a rare phenomena and potentially life-threatening complication of ERCP. Fewer than 55 cases worldwide have been published in regards to this [7, 9]. Whilst hemorrhage is a known side effect from ERCP, it is usually related to sphincterotomy. Bleeding from other areas such as spleen, liver and bowel are exceptionally rare. Whilst not proven, authors have reflected that the likely pathological mechanism for subcapsular hemorrhage is the ERCP guidewire causing a laceration to one or more intrahepatic vessels. Interestingly, in contrast to this hypothesis, there are cases of subcapsular hematomas where no guidewires have been used. The pathophysiology proposed in these cases is thought to be related to extractor balloon traction [10, 11].
A commonality in presentation of affected patients is the complaint of abdominal pain post-procedure. Pain may not be localized to the RUQ and all abdominal pain complaints should be taken seriously and investigated appropriately. In most cases, patients developed pain within 24 h as with this case. As such any patient with post-ERCP abdominal pain should be investigated appropriately for subcapsular hematoma. However, there are reported cases with a delay in the development of pain of several days and thus any patient re-presenting to hospital after ERCP should be investigated appropriately [12]. In cases without pain, cardiovascular instability, fevers and drops in hemoglobin are documented as the primary symptoms or signs [9].
Radiological modalities for diagnosis include abdominal ultrasound, CT and magnetic resonance imaging. However due to its relative ease of access, CT should potentially be proposed as the first-line imaging investigation. As well as imaging, serum tests such as hemoglobin, hematocrit and inflammatory markers are useful adjuncts for diagnosis but importantly do not exclude the diagnosis.
Management is largely supportive with most cases utilizing a non-operative approach. In combination with this, many cases reduce the risk of infected hematoma with IV antibiotics prophylactically. However, this case highlights that non-operative management is not always successful and percutaneous drainage or operative management has to be considered in unstable or septic patients already on IV antibiotics. The original treating team had opted for IR drainage but when this did not result in source control, the UGI surgeons were consulted.
Invasive treatment options should be considered for patients with cardiovascular instability, failure to improve, worsening sepsis, or evidence of on-going hemorrhage [8]. In this case, on-going sepsis and pain necessitated operative management. Interestingly, laparoscopic washout with necrosectomy of the subcapsular hematoma is not widely reported. Due to the extensive necrotic tissue and purulent material in the cavity found intraoperatively, decision was made to leave large abdominal drains in situ and commence continuous irrigation for several days.
Post-operatively, the patient made a swift clinical improvement. Undertaking necrosectomy and post-operative irrigation removed and controlled the significant septic foci. This, along with the prolonged course of IV antibiotics, allowed convalescence from the iatrogenic complication. In conclusion, this case highlights the necessary pragmatism required when managing a rare pathology and the flexibility needed to gain a successful outcome.
Learning points
Whilst extremely rare, subcapsular hepatic hematomas post-ERCP must be considered in patients with any post-procedural abdominal pain, cardiovascular instability, hemoglobin drop or fevers. Most resolve with non-operative management but IR and surgical intervention should be explored if patients become unstable or have worsening sepsis despite antibiotic therapy. Finally, we offer necrosectomy and continued irrigation as a potential safe treatment option for patients failing conventional treatments.
Acknowledgments
None to declare.
Financial Disclosure
None to declare.
Conflict of Interest
None to declare.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was gained prior to completing the case report.
Author Contributions
RP contributed to the conception, writing and editing of the case report. AD provided oversight to the case report.
Data Availability
The authors declare that data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
| References | ▴Top |
- Overview of gallstone disease in adults. UpToDate. [Cited 2021 Jan 5] https://www.uptodate.com.acs.hcn.com.au/contents/overview-of-gallstone-disease-in-adults?search=cholelithiasis&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1∼150&usage_type=default&acc=36422#H1.
- Everhart JE, Khare M, Hill M, Maurer KR. Prevalence and ethnic differences in gallbladder disease in the United States. Gastroenterology. 1999;117(3):632-639.
doi - European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL). Electronic address eee. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of gallstones. J Hepatol. 2016;65(1):146-181.
doi pubmed - Abdel Aziz AM, Lehman GA. Pancreatitis after endoscopic retrograde cholangio-pancreatography. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13(19):2655-2668.
doi pubmed - Cotton PB, Garrow DA, Gallagher J, Romagnuolo J. Risk factors for complications after ERCP: a multivariate analysis of 11,497 procedures over 12 years. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;70(1):80-88.
doi pubmed - Zizzo M, Lanaia A, Barbieri I, Zaghi C, Bonilauri S. Subcapsular Hepatic Hematoma After Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography: A Case Report and Review of Literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(26):e1041.
doi pubmed - Pivetta LGA, da Costa Ferreira CP, de Carvalho JPV, Konichi RYL, Kawamoto VKF, Assef JC, Ribeiro MA. Hepatic subcapsular hematoma post-ERCP: Case report and literature review. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2020;72:219-228.
doi pubmed - Zappa MA, Aiolfi A, Antonini I, Musolino CD, Porta A. Subcapsular hepatic haematoma of the right lobe following endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: Case report and literature review. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22(17):4411-4415.
doi pubmed - Caroco TV, Louro JM, Coelho MI, Costa Almeida CE. Rare case of hepatic haematoma following endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. BMJ Case Rep. 2018;2018.
doi pubmed - Tamez A, Cossio J, Hernandez G, Huezo M, Solis A, et al. Subcapsular hepatic hematoma: An unusual, but potentially life-threatening post-ERCP complication. Case Report and Literature Review. 2016;28:75-80.
doi - Baudet JS, Arguinarena X, Redondo I, Tadeo E, Navazo L, Mendiz J, Montiel R. [Subcapsular hepatic hematoma: an uncommon complication of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography]. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;34(2):79-82.
doi pubmed - Oliveira Ferreira A, Tato Marinho R, Velosa J. Infected hepatic hematoma 10 days after ERCP. Endoscopy. 2013;45(Suppl 2 UCTN):E402-403.
doi pubmed
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Medical Cases is published by Elmer Press Inc.


