| Journal of Medical Cases, ISSN 1923-4155 print, 1923-4163 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Med Cases and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.journalmc.org |
Case Report
Volume 8, Number 5, May 2017, pages 141-144
Ruptured Anaplastic Pancreatic Carcinoma With Liver Metastasis: A Case Report
Kazumasa Emoria, Nobuhiro Takeuchia, d, Makoto Yoshitania, Junichi Sonedaa, Kaori Mohrib, Yusuke Nomurac
aDepartment of Internal Medicine, Kobe Tokushukai Hospital, Tarumi, Kobe, Japan
bDepartment of Laboratory Medicine, Kobe Tokushukai Hospital, Tarumi, Kobe, Japan
cDepartment of Internal Medicine, Kawasaki Hospital, Kobe, Japan
dCorresponding Author: Nobuhiro Takeuchi, Department of Internal Medicine, Kobe Tokushukai Hospital, 1-3-10 Kamitakamaru, Tarumi-Ku, Kobe-shi, Hyogo 655-0017, Japan
Manuscript accepted for publication March 20, 2017
Short title: Ruptured Anaplastic Carcinoma of the Pancreas
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/jmc2802w
| Abstract | ▴Top |
A 65-year-old female with no relevant medical history visited our hospital with complaints of general fatigue and unlocalized abdominal pain. Non-contrast computed tomography revealed a tumor in the pancreatic tail, a diffusely swollen liver with obtuse vessel structure, and ascites above the liver surface and around the gallbladder. She went into cardiac arrest immediately after admission for further investigation of the tumor. Despite cardiopulmonary resuscitation, her spontaneous circulation could not be restored. An autopsy conducted with the consent of her family revealed 2,000 mL hemorrhagic ascites in the peritoneal cavity, a tumor measuring 4 × 2 × 2 cm in the pancreatic tail, accompanied by bleeding, and multiple sponge-like liver metastases. Microscopic examination of the pancreatic tumor and liver metastases revealed proliferation of sarcomatoid atypical cells (comprising spindle, pleomorphic, and giant cells) accompanied by red blood cells, necrosis, and fibrosis. Immunohistochemistry staining of the tumor was positive for cytokeratin (CK) AE1/AE3 and CK 7 and negative for CK 20. Thus, a diagnosis of anaplastic pancreatic carcinoma (APC), pleomorphic type, was established. From the autopsy findings, her death was concluded to be due to a hemorrhagic shock resulting from the ruptured APC. APC is a rare carcinoma among pancreatic malignancies and has a poor prognosis with rapid proliferation. Here we present an autopsy case of APC with multiple liver metastases where APC ruptured in the intraperitoneal cavity.
Keywords: Anaplastic pancreatic carcinoma; Liver metastasis; Rupture
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Anaplastic pancreatic carcinoma (APC) is a rare carcinoma among pancreatic malignancies, and it is known for its poor prognosis. Here we present an autopsy case of APC with multiple liver metastases where APC ruptured in the intraperitoneal cavity.
| Case Report | ▴Top |
A 65-year-old female visited our hospital with a complaint of general fatigue. She was a housewife with no past medical or family history and had been well before the clinical presentation. She denied any use of tobacco or alcohol. She had felt general fatigue for 3 weeks before presentation and had not seen a doctor until the symptoms had become intolerable.
Upon arrival, she was alert and complained of severe fatigue and dull pain over the upper abdomen, which was slightly distended with no tenderness. Cyanosis of the mouth and extremities was not apparent. Examination of the vital signs showed the following results: blood pressure, 110/42 mm Hg; heart rate, 80 beats/min; body temperature, 36.5 °C; and percutaneous oxygen saturation (SpO2), 98% under atmospheric air. An arterial blood gas analysis revealed metabolic acidosis (pH, 7.246; pCO2, 14.5 mm Hg; pO2, 142.1 mm Hg; HCO3-, 6.1 mmol/L; and base excess, 19.9 mmol/L). Blood analysis revealed an increased number of white blood cells (WBCs, 14,300 cells/μL), and moderately elevated lactate dehydrogenase (364 IU/L). No coagulation dysfunction was observed. Viral markers were negative for HBs-Ag, HCV-Ab, and TPHA. Tumor makers were within normal limits (CEA, 3.6 ng/mL; CA19-9, 20.4 U/mL; and AFP 3.3 ng/mL).
Non-contrast computed tomography revealed a diffusely swollen liver with obscure vessel structures, a mass in the pancreatic tail, and ascites around the gall bladder and liver (Fig. 1a, b, c).
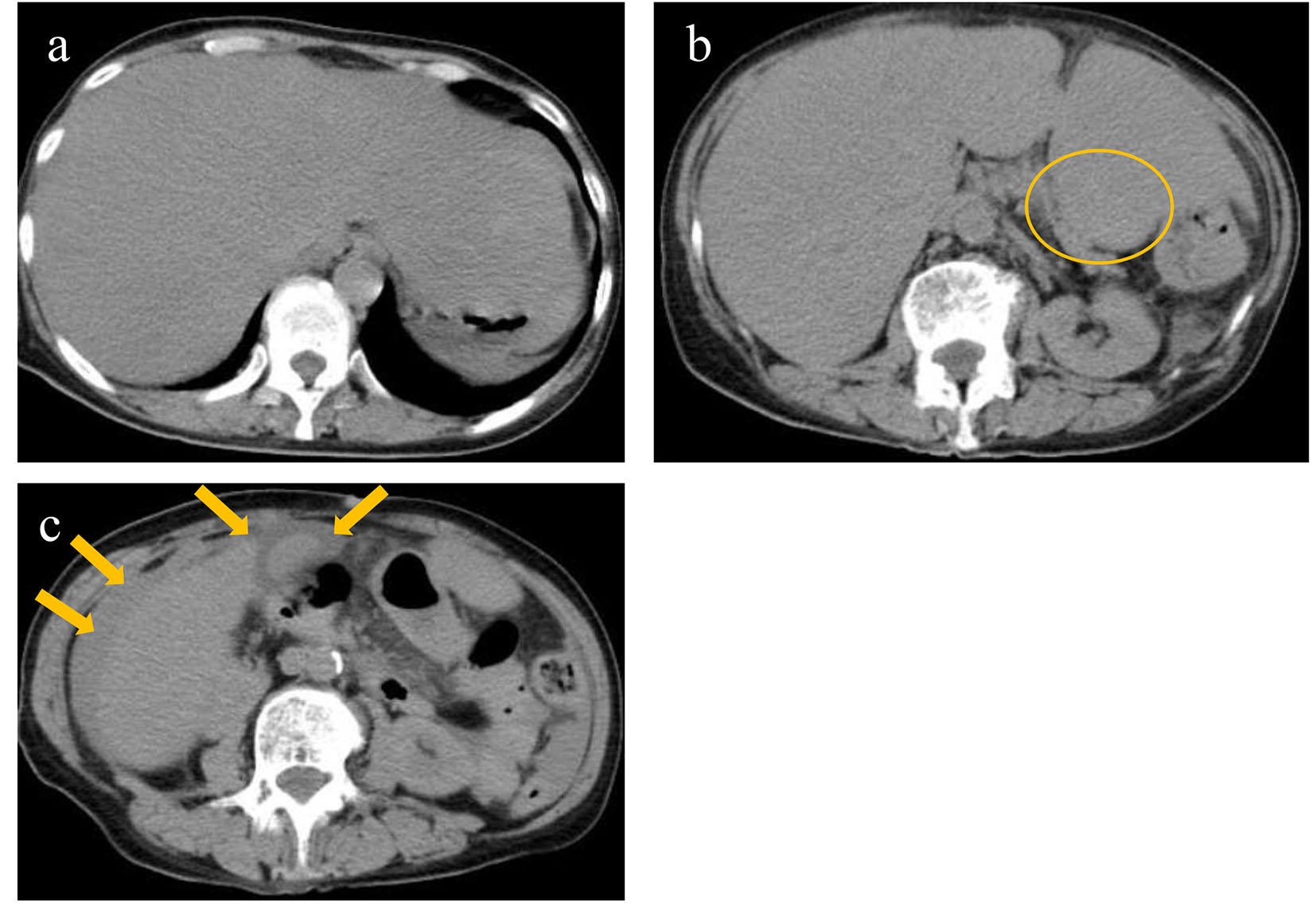 Click for large image | Figure 1. Non-contrast computed tomography revealed diffusely swollen liver with obscure vessel structures (a), a mass in the pancreatic tail (circle) (b), and ascites around the gall bladder and liver (arrows) (c). |
The patient was admitted for further examination of her symptoms. Immediately after admission, she complained of throbbing pain in the upper abdominal. Within an hour, she suddenly went into cardiac arrest. Emergency laboratory analysis revealed decreased red blood cells (RBCs, 248 × 104/μL; hemoglobin levels, 7.9 g/dL). Despite our efforts to revive the patient with cardiopulmonary resuscitation, her spontaneous circulation could not be restored.
An autopsy was performed after the consent of her family. Approximately 2,000 mL hemorrhagic ascites was revealed in the peritoneal cavity. A tumor (measuring 4 × 2 × 2 cm) accompanied by hemorrhage was discovered in the pancreatic tail (Fig. 2a). Furthermore, multiple sponge-like tumors were observed in the liver (Fig. 2b). The tumor was found to proliferate by replacing normal liver tissues. Microscopic specimens of the pancreatic tumor revealed proliferation of sarcomatoid atypical cells (comprising spindle, pleomorphic, and giant cells), accompanied by RBCs, necrosis, and fibrosis (Fig. 2c). Microscopic specimens of the liver tumors revealed sarcomatoid atypical cells (identical to those in the pancreatic tumor) along with severely necrotized tissues in the liver sinusoids (Fig. 2d). Immunohistochemical staining of the tumor was positive for cytokeratin (CK) AE1/AE3 and CK 7 and negative for CK 20, suggesting that the tumor derived from epithelial tissues (Fig. 3a, b, c). From these findings, a diagnosis of primary APC, pleomorphic type, with multiple liver metastases was established. It was concluded that the patient’s death was caused by hemorrhagic shock due to the ruptured pancreatic cancer.
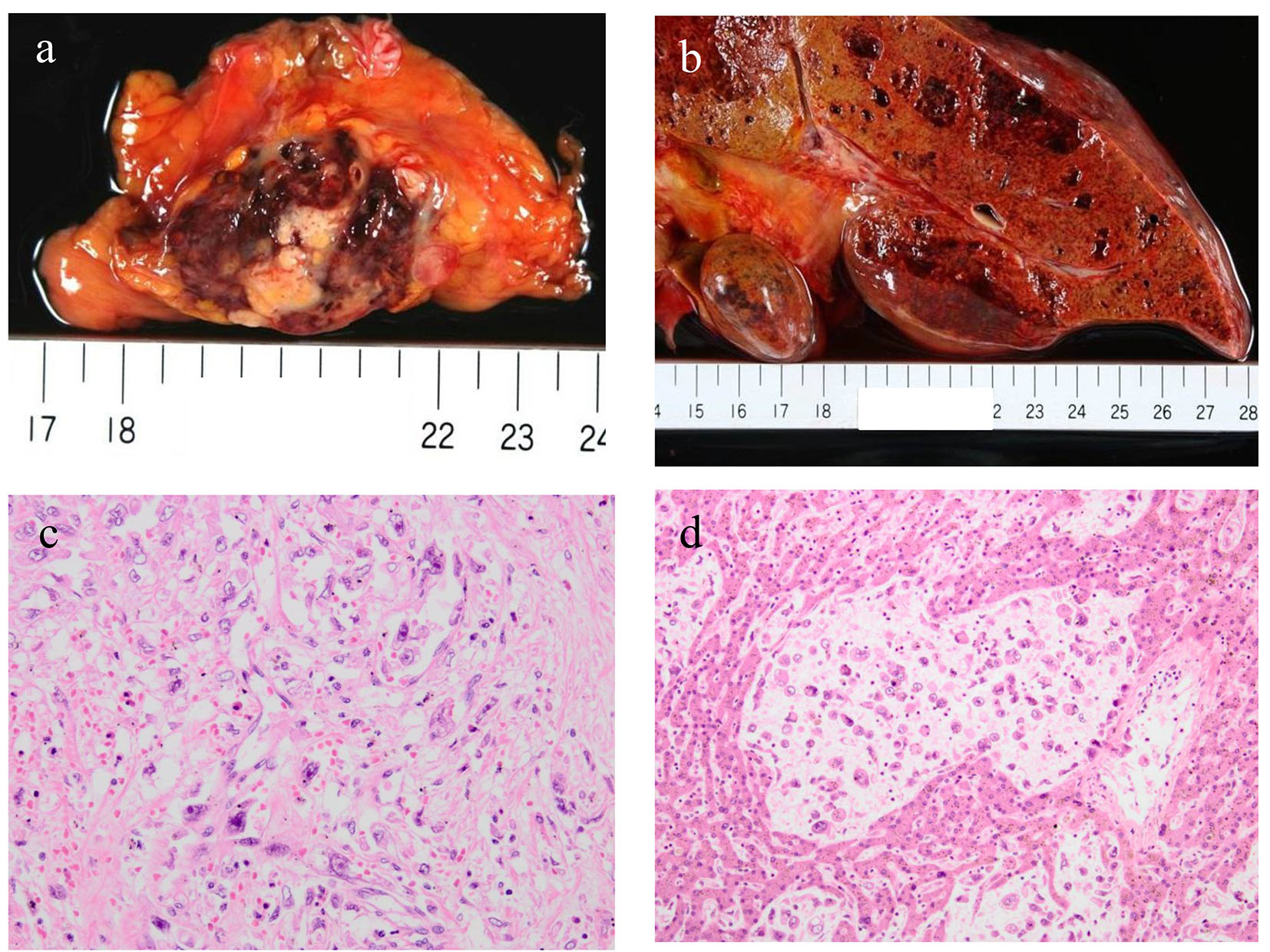 Click for large image | Figure 2. An autopsy revealed a tumor measuring 4 × 2 × 2 cm in the pancreatic tail accompanied by hemorrhage (a) and multiple sponge-like tumors in the liver (b). Microscopic specimens of the pancreatic tumor (c) and liver metastases (d) revealed proliferation of sarcomatoid atypical cells (comprising spindle, pleomorphic, and giant cells) accompanied by red blood cells, necrosis, and fibrosis. |
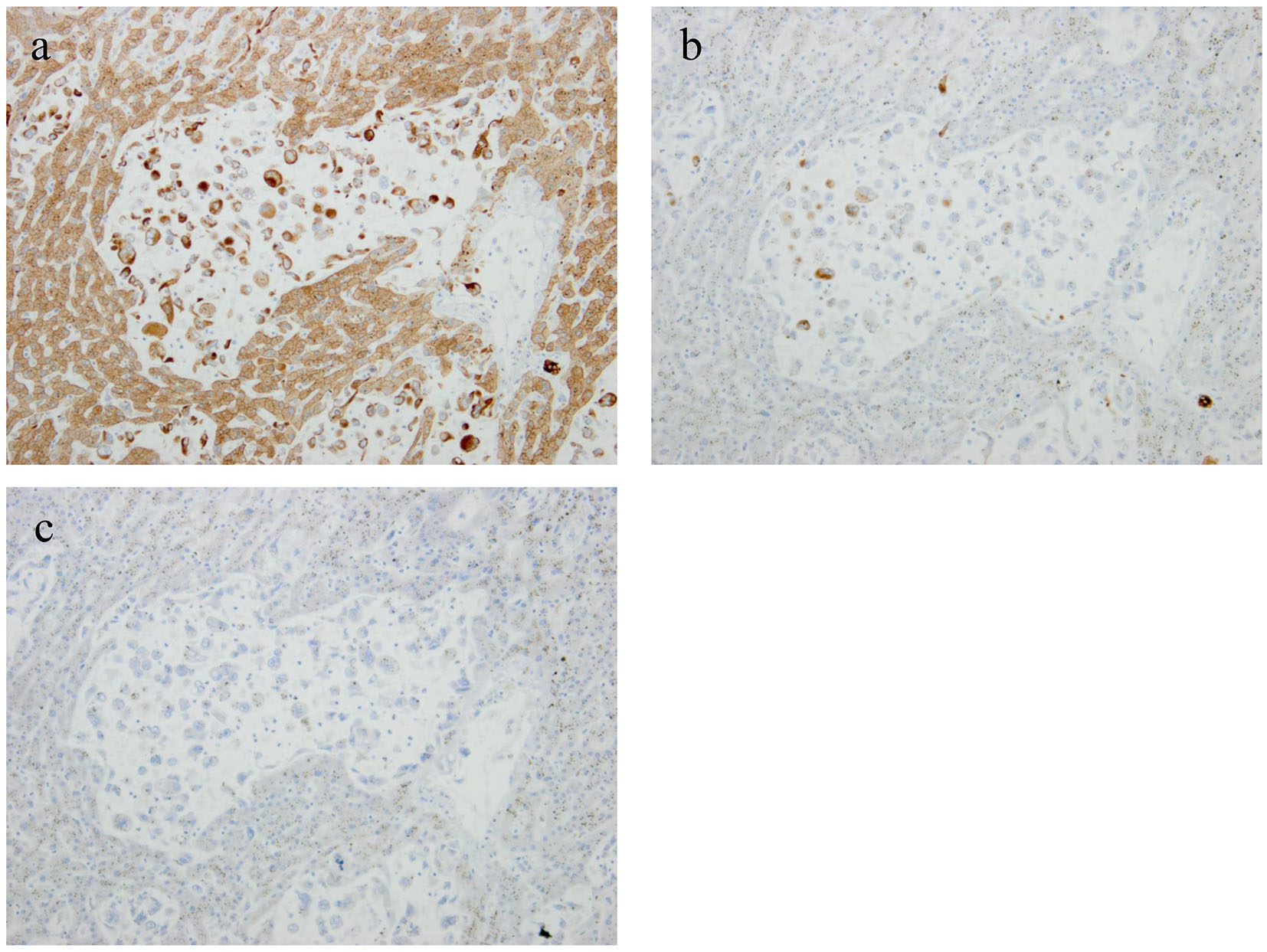 Click for large image | Figure 3. Immunohistochemical staining of the tumor was positive for cytokeratin (CK) AE1/AE3 and CK 7 and negative for CK 20, suggesting the tumor derived from epithelial tissues (a: CK AE1/AE3; b: CK 7; c: CK 20). |
| Discussion | ▴Top |
APC was first reported by Sommer in 1954 as a pleomorphic carcinoma of the pancreas [1]. APC comprises a combination of spindle, pleomorphic, and giant cells and is characterized by sarcomatoid proliferation and bleeding necrosis [1]. It is an uncommon carcinoma accounting for 2-7% of all pancreatic malignancies and predominantly occurs in males [2, 3]. The biological nature of APC is characterized by a more expansive growth, richer vascularity, and larger size than the pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) [4].
In Japan, APC has been classified as a form of invasive PDAC because it contains some components of PDAC [5]. Pathological characteristics of APC are as follows: 1) components of PDAC are included and transition to sarcomatoid components is distinguishable; 2) epithelial structures like desmosomes can be observed in sarcomatoid cells through an electronmicroscopy, and 3) immunohistochemical staining using epithelial markers, including CK and EMA, shows positive results [6]. Thus, APC is considered to dedifferentiate from the differentiated adenocarcinoma, although it has sarcomatoid features and is a form of PDAC. APC is subclassified according to the cell structure as spindle, pleomorphic, or giant cell type. Among these, the giant cell type, which resembles phagocytic or osteoid cells, is differentiated as giant cell carcinoma of the osteoid type. The pleomorphic cell type is characterized by a combination of highly atypical mononuclear or multinuclear cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm, atypical spindle cells with varied nuclei, and giant cells with remote proliferation.
The clinical manifestations are not different between APC and PDAC; back pain, weight loss, and abdominal distention are the major symptoms. There have been few case reports of APC that presented with the rupture of the tumor into the peritoneal cavity [7, 8]. Considering the pathological nature of APC, which grows rapidly and is rich vascularity, it is plausible that spontaneous rupture of the tumor may occur, albeit infrequently. In addition, the invasion of APC into surrounding vessels may cause bleeding.
The diagnosis of APC using imaging modalities can sometimes be challenging. Using CT, it is difficult to differentiate APC from PDAC, intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm, and mucinous cystic neoplasm as well as from gastrointestinal stromal tumor and leiomyosarcoma in the stomach. In general, using contrast-enhanced CT, the radiological findings of APC are characterized by a central low-density area encircled by hypervascular margins, suggesting central necrosis or bleeding necrosis. However, about two-fifths of APCs reveal marginal vascular stains around a necrotic tumor. Other findings are arterial encasement and stenosis of the pancreatic duct with peripheral dilatation although these findings are also observed in PDAC.
The prognosis of APC is poorer than that of PDAC because of its aggressive nature and extensive hematogenous dissemination. One-year fatality rates are 71%, and 5-year survival rates are 9.6% only [7]. The major metastatic lesion of APC presents in the liver (87%), followed by the lungs (73%), adrenal glands (60%), kidneys (47%), bones (40%), heart (33%), and thyroid gland (20%) [2].
The mainstay of treatment for APC is surgical resection because of a poor response to chemotherapy or radiotherapy. The fatality observed 3 months after the surgical intervention is reported to be 58.6%, and the average survival period is 5.5 months. Surgical intervention for APC is controversial because of the poor survival rate despite the complete removal of the tumor [8]. The majority of APCs are detected at an advanced stage and a combined resection of the invaded organs is frequently required.
Although the rupture of APC into the peritoneal cavity, efforts should be made to detect the rupture before the patient goes into hemorrhagic shock. Although contrast-enhanced CT or angiography was not performed in our presented case, these should be considered in a suspected case to reveal the potential rupture of a tumor upon patient arrival. This autopsy case is helpful in raising awareness among clinicians to unveil the medical conditions of a patient with unknown gastrointestinal symptoms and suspected tumors in an emergency setting.
Conclusion
We reported a rare case of APC that ruptured into the peritoneal cavity, leading to hemorrhagic shock. This case report may help clinicians to remember the rare condition of a pancreatic tumor and the necessity of rapidly evaluating the cause of the tumor unless non-contrast CT provides effective information.
Consent
The family of the patient gave written informed consent for publication of this case report and all accompanying images.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
| References | ▴Top |
- Sommers SC, Meissner WA. Unusual carcinomas of the pancreas. AMA Arch Pathol. 1954;58(2):101-111.
pubmed - Tschang TP, Garza-Garza R, Kissane JM. Pleomorphic carcinoma of the pancreas: an analysis of 15 cases. Cancer. 1977;39(5):2114-2126.
doi - Paal E, Thompson LD, Frommelt RA, Przygodzki RM, Heffess CS. A clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 35 anaplastic carcinomas of the pancreas with a review of the literature. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2001;5(3):129-140.
doi pubmed - Yamaguchi K, Nakamura K, Shimizu S, Yokohata K, Morisaki T, Chijiiwa K, Tanaka M. Pleomorphic carcinoma of the pancreas: reappraisal of surgical resection. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998;93(7):1151-1155.
doi pubmed - Japan pancreas society: pancreatic cancer registry report 2007. J Jpn Pancreas Soc. 2007;22.
- Kubo M, Takao S, Shinchi H, Uchikura K, Higashi M, Yonezawa S, Aikou T. Spindle cell carcinoma of the pancreas. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2000;7(2):236-241.
doi pubmed - Matumura Y, Iwai K, kawasaki R, et al. A case of spontaneously ruptured anaplastic carcinoma (giant cell type) of the pancreas. Jpn J Gastroenterol Surg. 2007;40(4):456-461.
doi - Suzuki S, Harada N, Suzuki M, et al. A case of pleomorphic carcinoma of the pancreas. J Jpn Pancreas Soc. 2007;22(2):137-142.
doi
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Medical Cases is published by Elmer Press Inc.


