| Journal of Medical Cases, ISSN 1923-4155 print, 1923-4163 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Med Cases and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.journalmc.org |
Case Report
Volume 4, Number 1, January 2013, pages 43-45
A Rare Presentation of Stroke: Basilary Artery Dissection
Fevzi Yilmaza, c, Engin Deniz Arslana, Miray Ozlema, Cemil Kavalcia, Deniz Sonmez Cilizb, Bige Sayin Severb
aEmergency Medicine Departmant, Ankara Numune Education and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey
bRadiology Departmant, Ankara Numune Education and Research Hospital, Ankara, Turkey
cCorresponding author: Fevzi Yilmaz, Ankara Numune Education and Research Hospital 06100 Altindag, Ankara, Turkey
Manuscript accepted for publication September 24, 2012
Short title: Basilary Artery Dissection
doi: https://doi.org/10.4021/jmc898w
| Abstract | ▴Top |
Basilar artery (BA) dissection has significant morbidity and mortality and the diagnosis of BA dissection is difficult. It should be considered as a differential diagnosis particularly in young adults with subarachnoid hemorrhage and stroke at the watershed area of posterior circulation. An 18 year old male patient presented to our Emergency Department (ED) with complaints related to loss of consciousness, altered mental status and visual disturbances following masturbation. Basilar artery dissection diagnosed based on imagining studies. This is thought to be the first case of basilar artery dissection presented resulting from masturbation.
Keywords: Stroke; Basilar artery dissection; Masturbation
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Cervicocerebral artery dissection accounts for approximately 2% all ischemic strokes in all ages but in young patients with ischemic stroke, arterial dissection ratios rise up to 10-25% [1]. The overall incidence of basilar artery dissection is approximately 1-1.5 in 100,000 [2, 3]. Little is known about clinical course and prognosis. We report a basilar artery dissection case developed following masturbation.
| Case Report | ▴Top |
An 18-year-old male patient presented to our emergency department (ED) with complaints related to syncope, altered mental status and visual disturbances. Patient’s history revealed that the patient was found unconscious in the toilet by family members. The patient did not have recent history of trauma and his medical history was unremarkable. His vital signs upon presentation were stable. Neurological exam revealed tendency to sleep, ataxia and right sided inability. Deep tendon reflexes were hypoactive. CBC, liver and kidney function tests, arterial blood gases, coagulation profiles, serum erythrocyte sedimentation rate, rheumatoid factor, VDRL, protein C, protein S, Factor 8, antinuclear antibody, fibrinogen, and fibrinogen degradation factors were all unremarkable within normal ranges. Uncontrasted Cranial Tomography (CT) was unremarkable. On evaluation of cranial diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance image (MRI), a lesion was observed in the left thalamus primarily thought to be acute ischemic stroke (Fig. 1). During his follow up his mental status improved gradually and the patient mentioned masturbation as the last event before his loss of consciousness. The patient had normal transthoracic echocardiography findings and the duplex ultrasound showed normal blood flow in both carotid and vertebral arteries bilaterally.
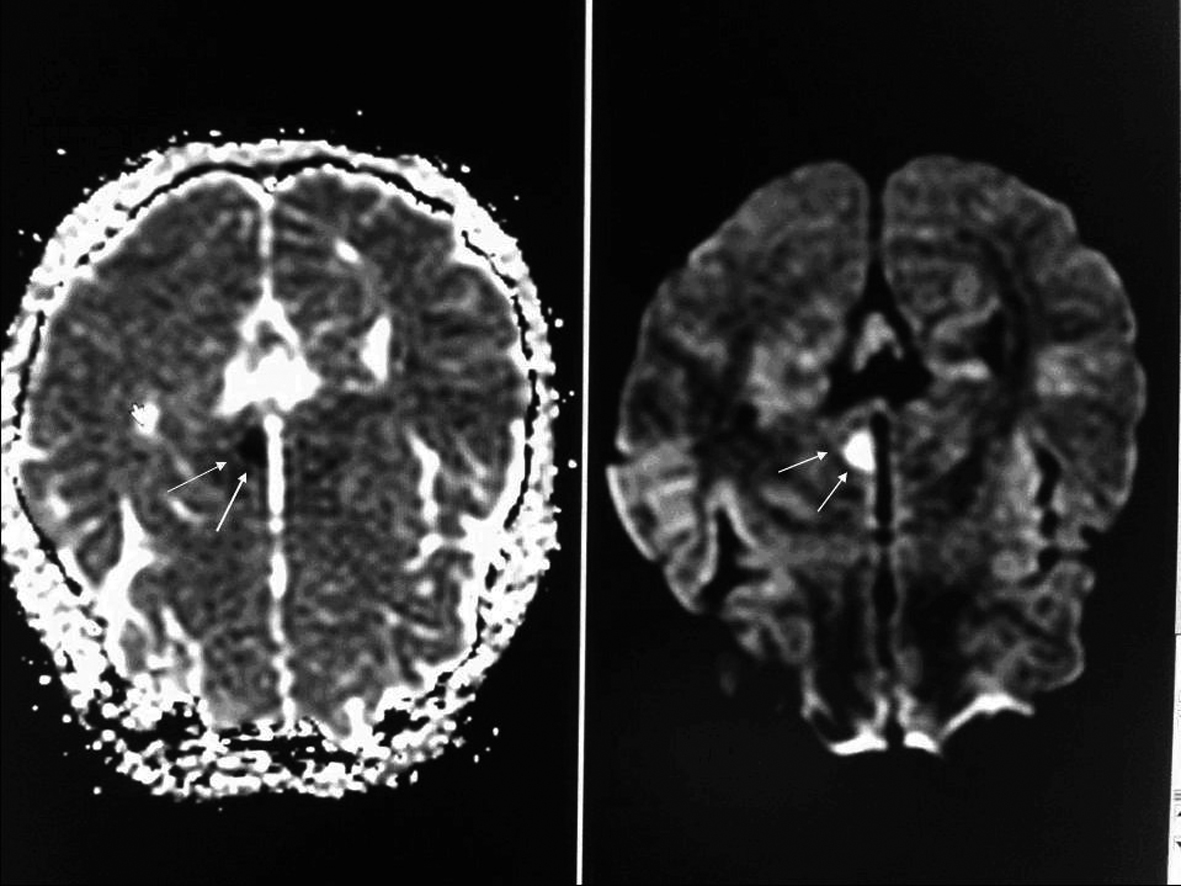 Click for large image | Figure 1. On evaluation of cranial diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance image (MRI), a lesion region slightly hypodense in T1A and slightly hyperdense in T2A series and primarily thought to be acute ischemic was observed in the left thalamus. |
A three-dimensional computed tomographic angiography (CTA) of the head showed narrowing of the basilar artery from the distal ends of the anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) branches to posterior cerebellar artery (PCA) in volume rendered (VR) images. There was also narrowing in the left PCA P1 segment as well as right PCA P1 and P2 segments (Fig. 2). Vertebrobasilar angiography was performed with Digital Substraction Angiography (DSA) and reduction in artery calibration at AICA exit in the distal end of the basilary artery was seen following the vertebral artery injection in anterior posterior plane (String sign) (Fig. 3). There were also thinning of the lumen, flap and filling of the false lumen observed along with the real vessel calibration in lateral projection indicating artery dissection and the diagnosis was made basilar artery dissection resulting in left thalamus infarction (Fig. 4). The patient was started on Coraspin 300 mg per orally and subcutaneous low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH). He was discharged without sequalae on 10th day of admission and was prescribed warfarin.
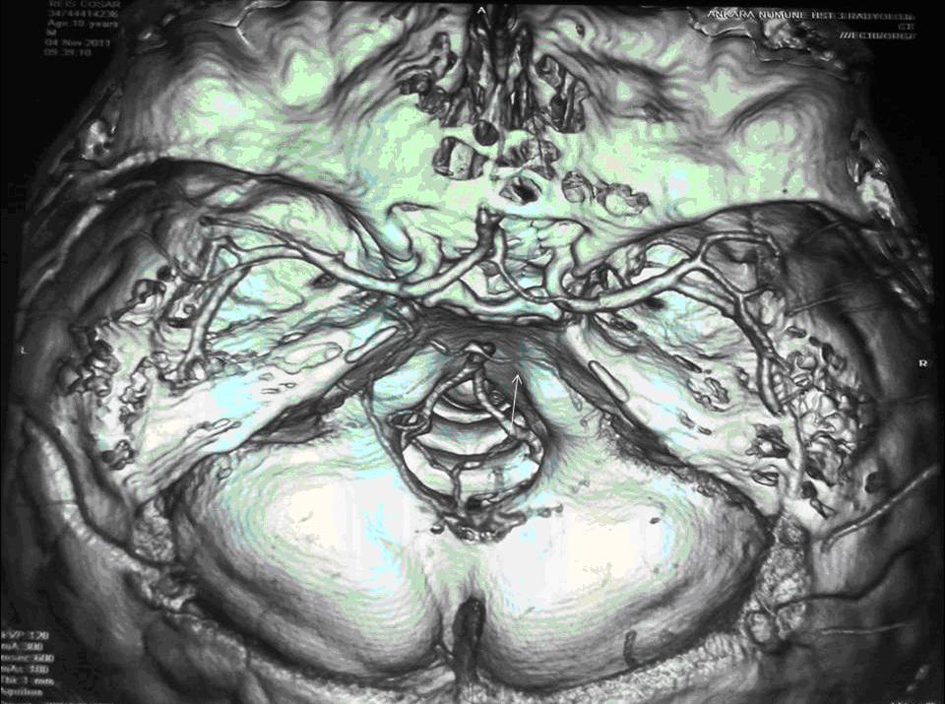 Click for large image | Figure 2. A three-dimensional computed tomographic angiography (CTA) of the head showed narrowing of the basilar artery from the distal ends of the anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) branches to posterior cerebellar artery (PCA) in volume rendered (VR) images. There was also narrowing in the left PCA P1 segment as well as right PCA P1 and P2 segments. |
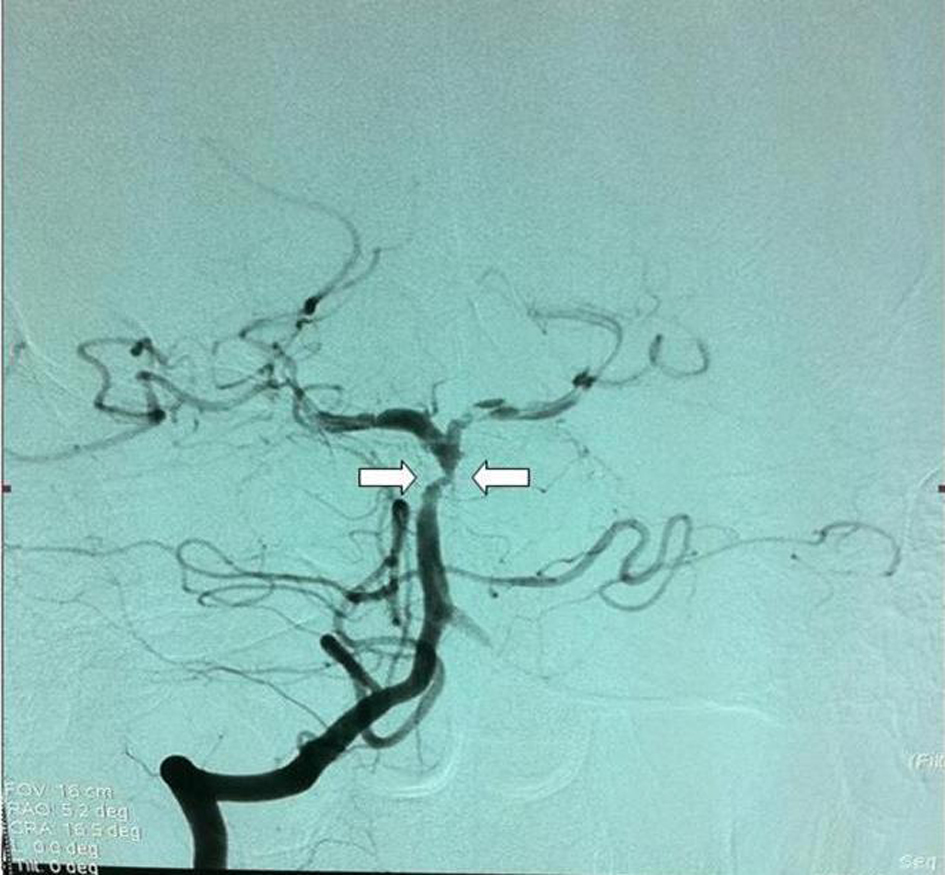 Click for large image | Figure 3. Vertebrobasilar Digital Substraction Angiography (DSA) and reduction in artery calibration at AICA exit in the distal end of the basilary artery was seen following the vertebtal artey injection in anterior posterior plane. |
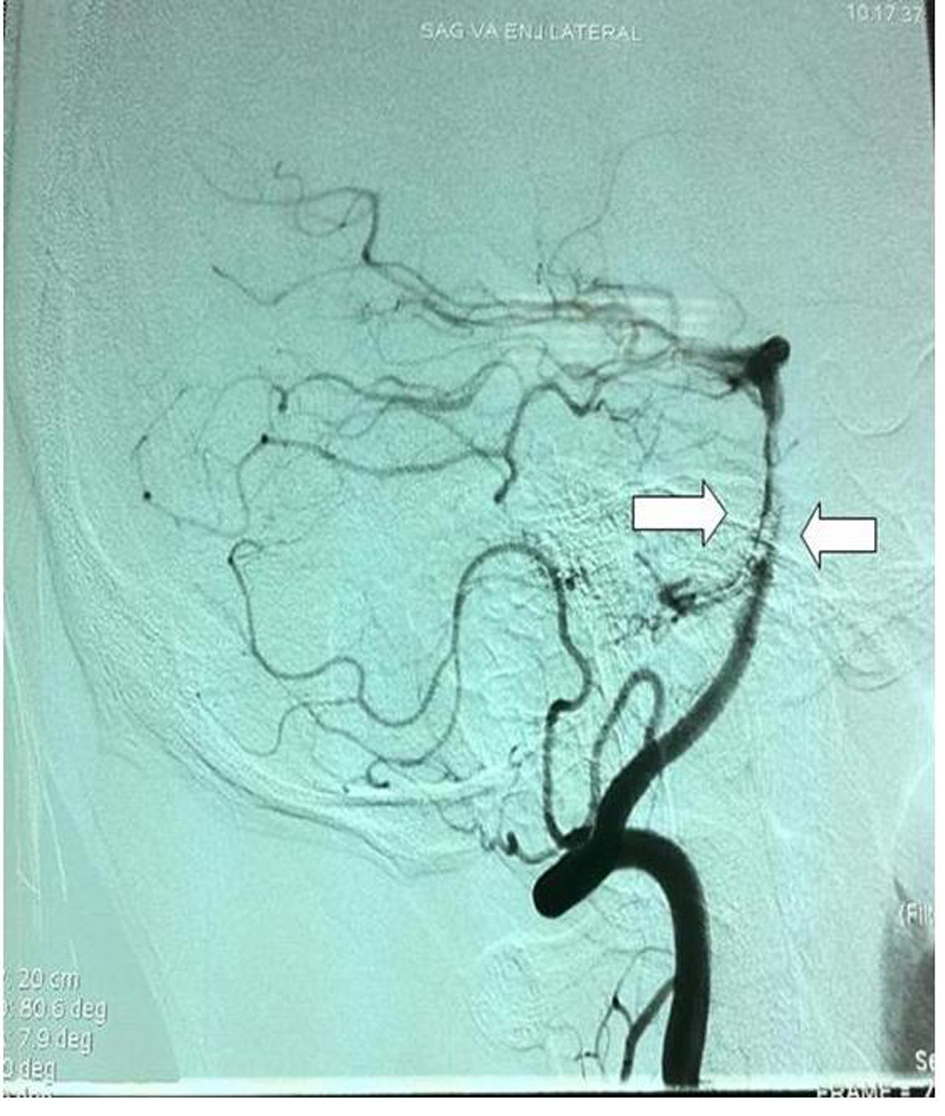 Click for large image | Figure 4. Thinning of the lumen (String sign), flap and filling of the false lumen observed along with the real vessel calibration in lateral projection. |
| Discussion | ▴Top |
The hallmark of dissection is subintimal tears which causes hemorrhage, further development of an intramural hematoma and embolisation from the site of dissection resulting in ischemia. Blunt trauma to the head and neck, arteriopathies including fibromuscular dysplasia, marfan syndrome, ehlers-danlos syndrome, cystic medial necrosis, meningovascular syphilis are associated with cervicocerebral dissections [1]. We were not able to detect any one of these conditions in our patient. Presence of a familial history or a recent infection was also negative. However sexual activity is also associated with dissections and our patient revealed history of sexual activity [4]. Neurological conditions precipitated by sexual activity include transient global amnesia, monocular blindness, syncope, subarachnoid hemorrhage, intracranial hematoma, embolic strokes, and severe headaches [5]. It is thought to be the result of sudden rise in blood pressure that occurs at time of orgasm [6, 7]. To the best of our knowledge, we are not aware of a case of basilar artery dissection resulting from masturbation reported in the literature.
Most cases of basilar artery dissections were aged 20 - 45 years with male predominancy and our patient fit the risk model descripted in the literature [8].
Extracranial dissections have tendency to bleed opposed to intracranial dissections that are associated with ischemic lesions as occurred in our patient [9, 10].
Magnetic resonance, Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) and CT Angiography are the diagnostic tools for these conditions. When other methods fail, conventional DSA is still considered as gold standard for diagnosis [1].
Even though conservative treatment approach including anticoagulation and controlling blood pressure is preferred by some authorities, cases with progressive symptoms resistant to medical therapies, or when anticoagulant treatment is contraindicated or which the dissections require surgical or endovascular treatment [2, 3].
Clinical course and the prognosis are not well known. Prognosis is first determined by the initial presentation of the patient [9, 10]. Prognosis in patients with brain ischemia is thought to be better according to presence of subarachnoid hemorrhage [9]. Our patient presented with ischemic symptoms, recived conservative treatment and discharged without sequalae.
Conclusion
Basilar artery dissection is a rare but life threatening condition. It should be considered among differential diagnosis particularly in young patients presenting with stroke. Early diagnosis and treatment may reduce the severe neurological complications to a great degree.
| References | ▴Top |
- Han Z, Leung TW, Lam W, Soo Y, Wong KS. Spontaneous basilar artery dissection. Hong Kong Med J. 2007;13(2):144-146.
pubmed - Kim BM, Suh SH, Park SI, Shin YS, Chung EC, Lee MH, Kim EJ, et al. Management and clinical outcome of acute basilar artery dissection. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29(10):1937-1941.
pubmed doi - Yoon WK, Kim YW, Kim SR, Park IS, Kim SD, Jo KW, Baik MW. Angiographic and clinical outcomes of stent-alone treatment for spontaneous vertebrobasilar dissecting aneurysm. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2010;152(9):1477-1486; discussion 1486.
pubmed doi - Szatmary Z, Boukobza M, Vahedi K, Stapf C, Houdart E, Bousser MG. Orgasmic headache and middle cerebral artery dissection. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2006;77(5):693-694.
pubmed doi - Jacome DE. Masturbatory-orgasmic extracephalic pain. Headache. 1998;38(2):138-141.
pubmed doi - Delasobera BE, Osborn SR, Davis JE. Thunderclap headache with orgasm: a case of basilar artery dissection associated with sexual intercourse. J Emerg Med. 2012;43(1):e43-47.
pubmed doi - Joo IS, Lee JS. Dissecting aneurysm of the basilar artery as a cause of orgasmic headache. Headache. 2005;45(7):956-959.
pubmed doi - Berkovic SF, Spokes RL, Anderson RM, Bladin PF. Basilar artery dissection. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1983;46(2):126-129.
pubmed doi - Yoshimoto Y, Hoya K, Tanaka Y, Uchida T. Basilar artery dissection. J Neurosurg. 2005;102(3):476-481.
pubmed doi - Ruecker M, Furtner M, Knoflach M, Werner P, Gotwald T, Chemelli A, Zangerle A, et al. Basilar artery dissection: series of 12 consecutive cases and review of the literature. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2010;30(3):267-276.
pubmed doi
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Medical Cases is published by Elmer Press Inc.


