Figures
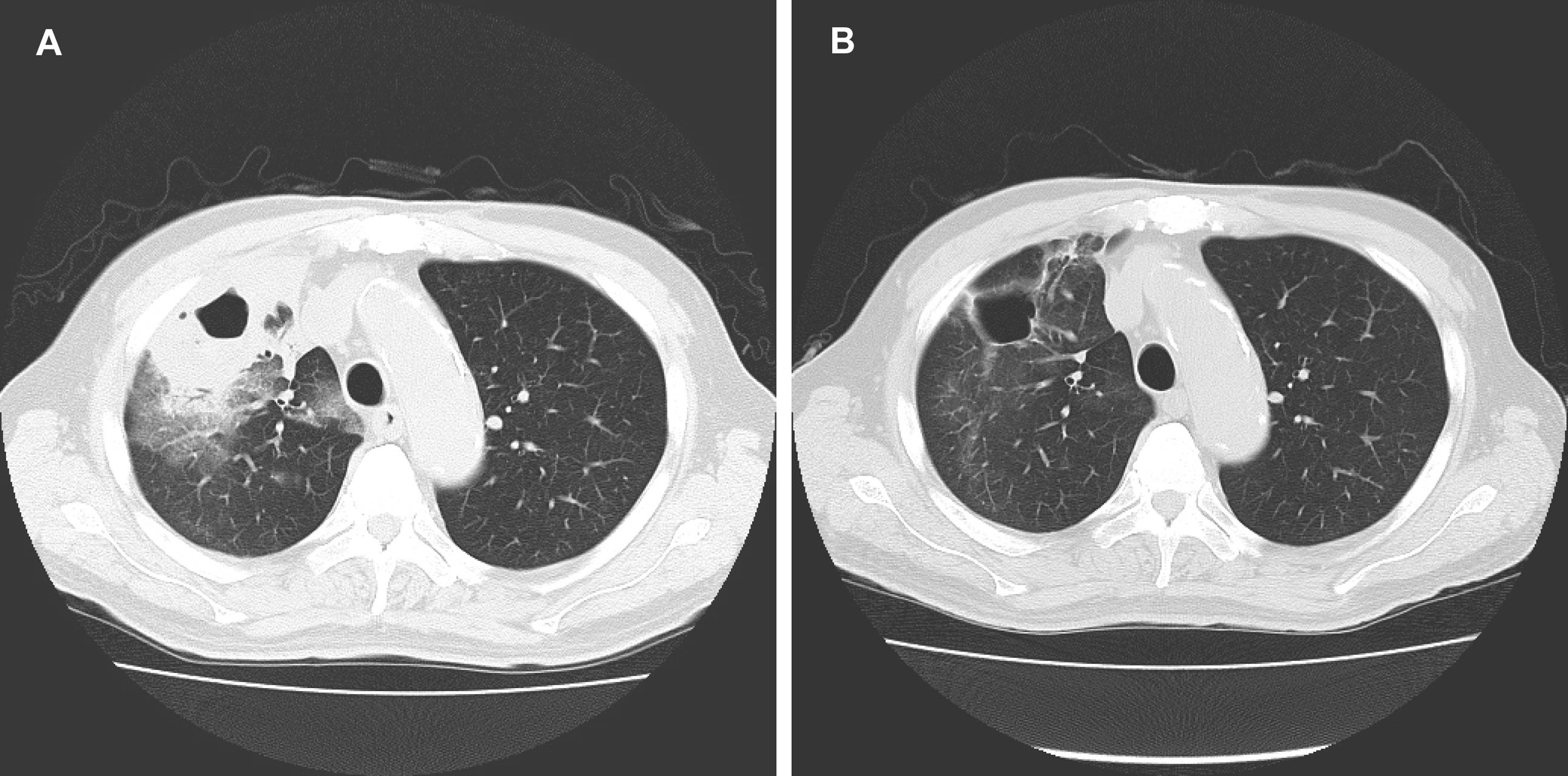
Figure 1. (A) Chest CT showed a lung abscess in right S3; (B) Chest CT showed a cavitary lesion, but the fluid accumulation resolved.
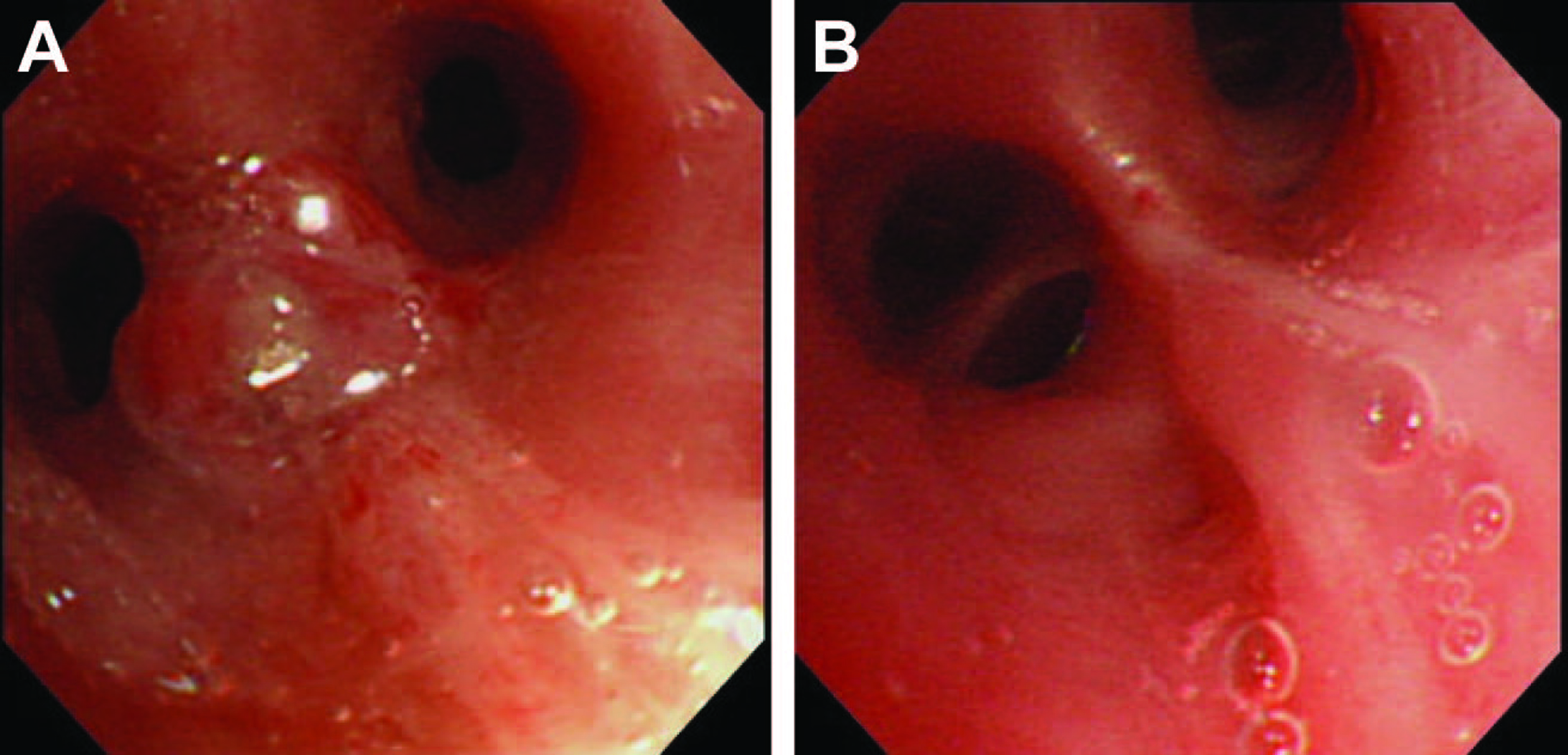
Figure 2. (A) Bronchoscopic findings was a protruding lesion at the opening of right B3, with stenosis of the involved bronchus; (B) A bronchoscopy on day 24 was disappearance of the protruding lesion at the opening of right B3, with improvement of the luminal stenosis.
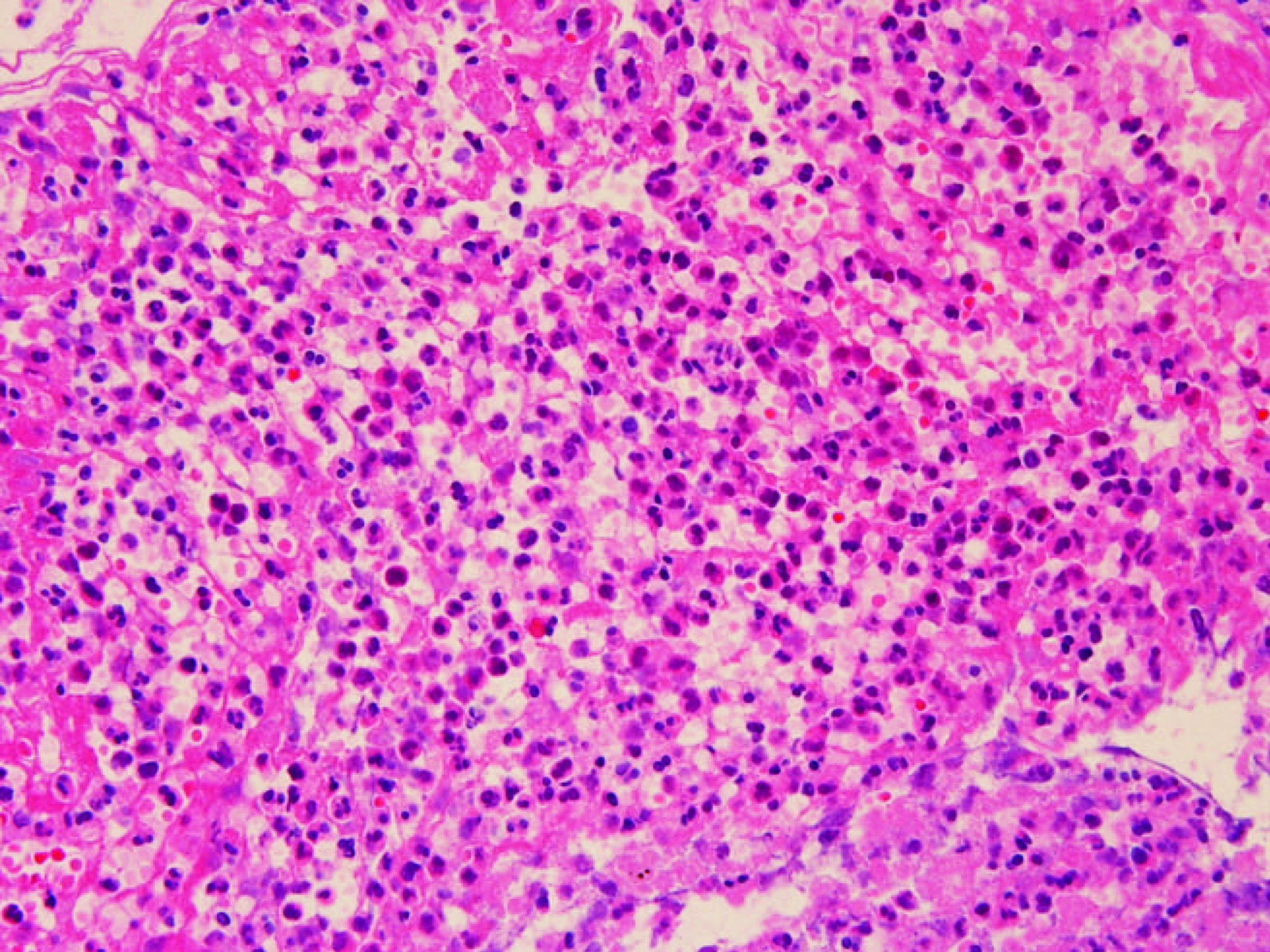
Figure 3. The histological findings obtained from bronchial biopsy were extensive neutrophilic infiltration in the submucosal tissue. In some areas, there was inflammatory cell infiltration together with fibroblast proliferation.
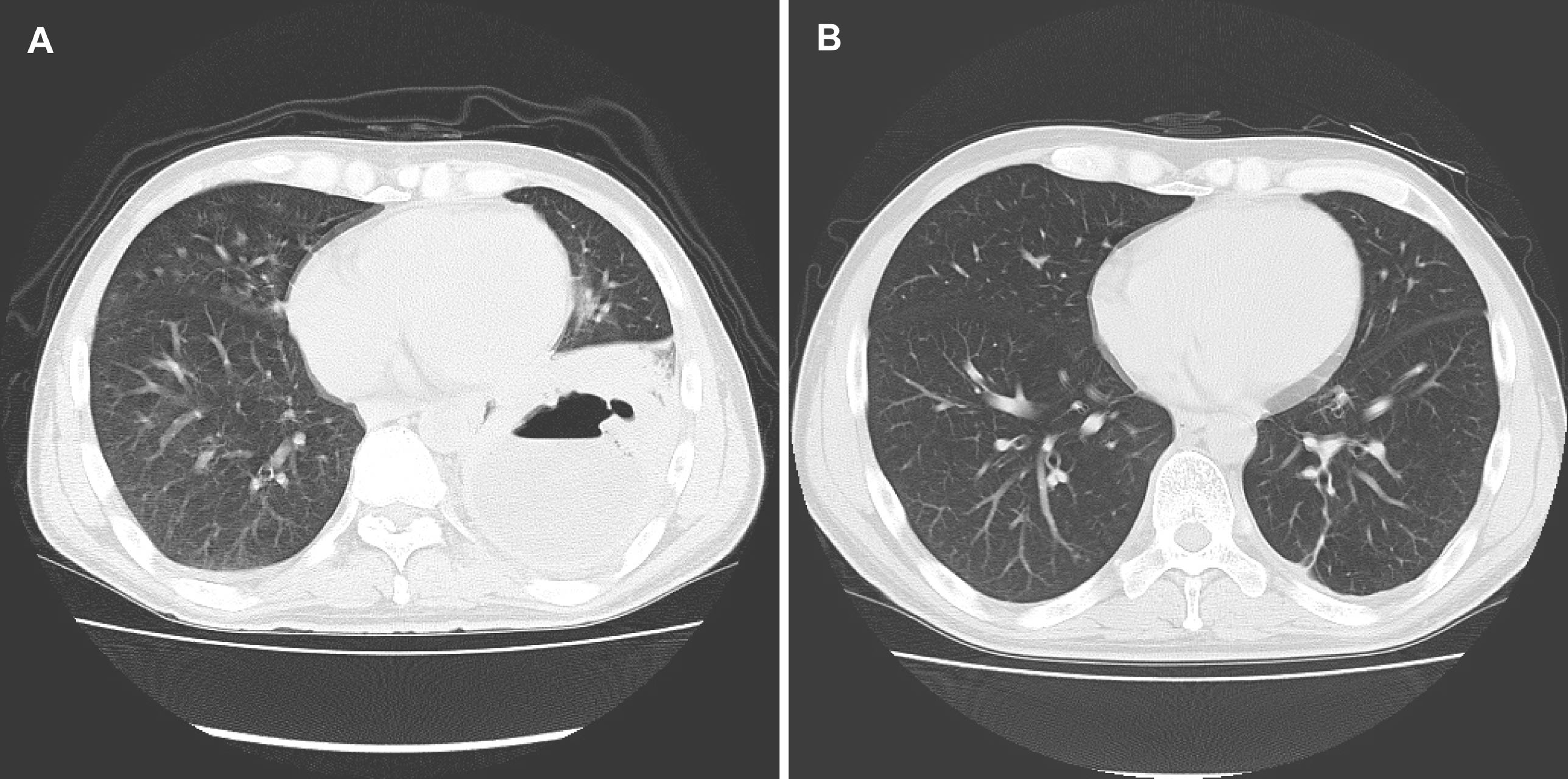
Figure 4. (A) Chest CT showed a lung abscess in left S10; (B) Chest CT showed improvement of the lung abscess.
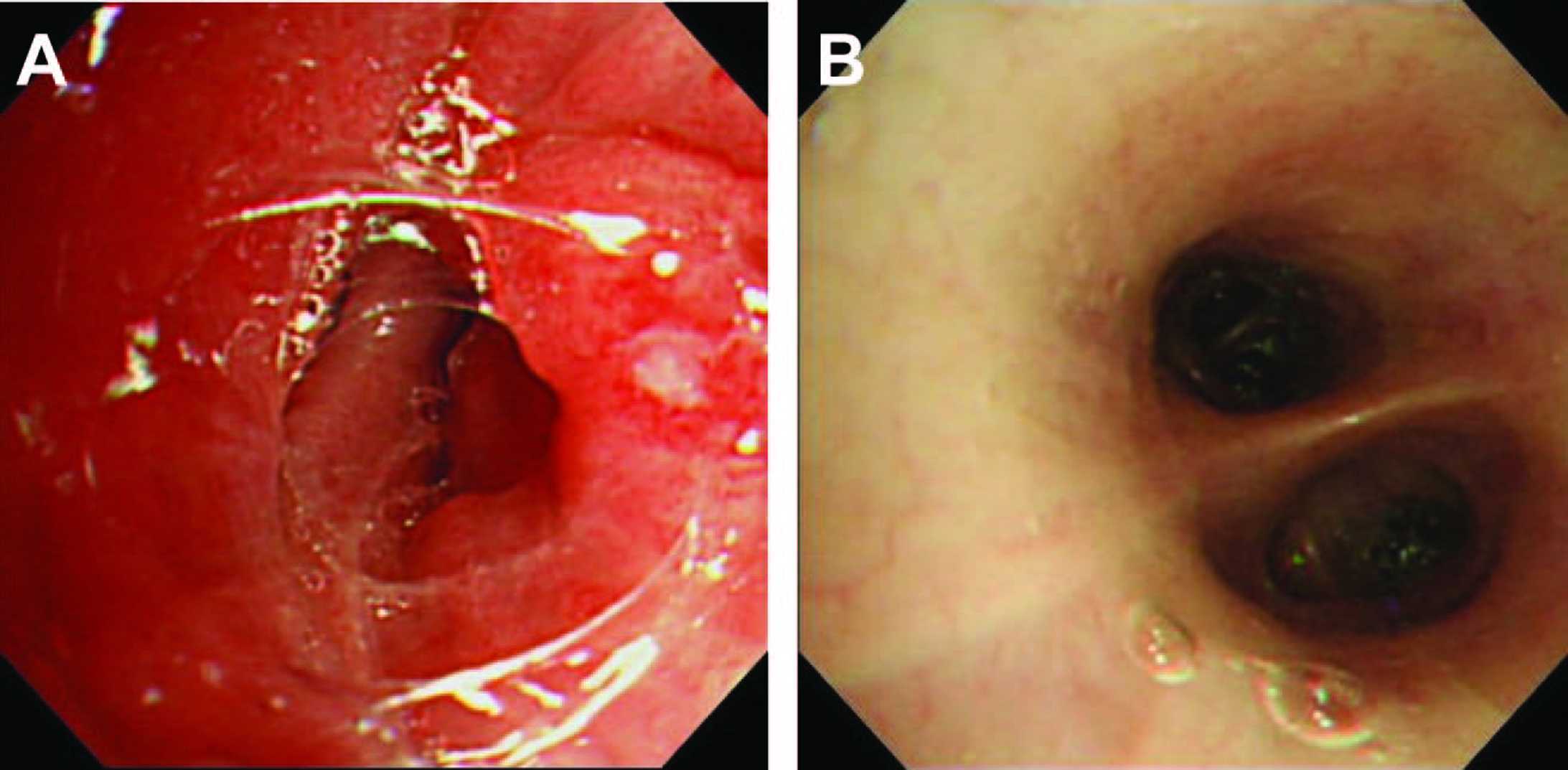
Figure 5. (A) Bronchoscopic findings were a protruding lesion at the opening of left B10, and the lumen was stenosed; (B) A bronchoscopy on day 28 revealed no abnormal findings.
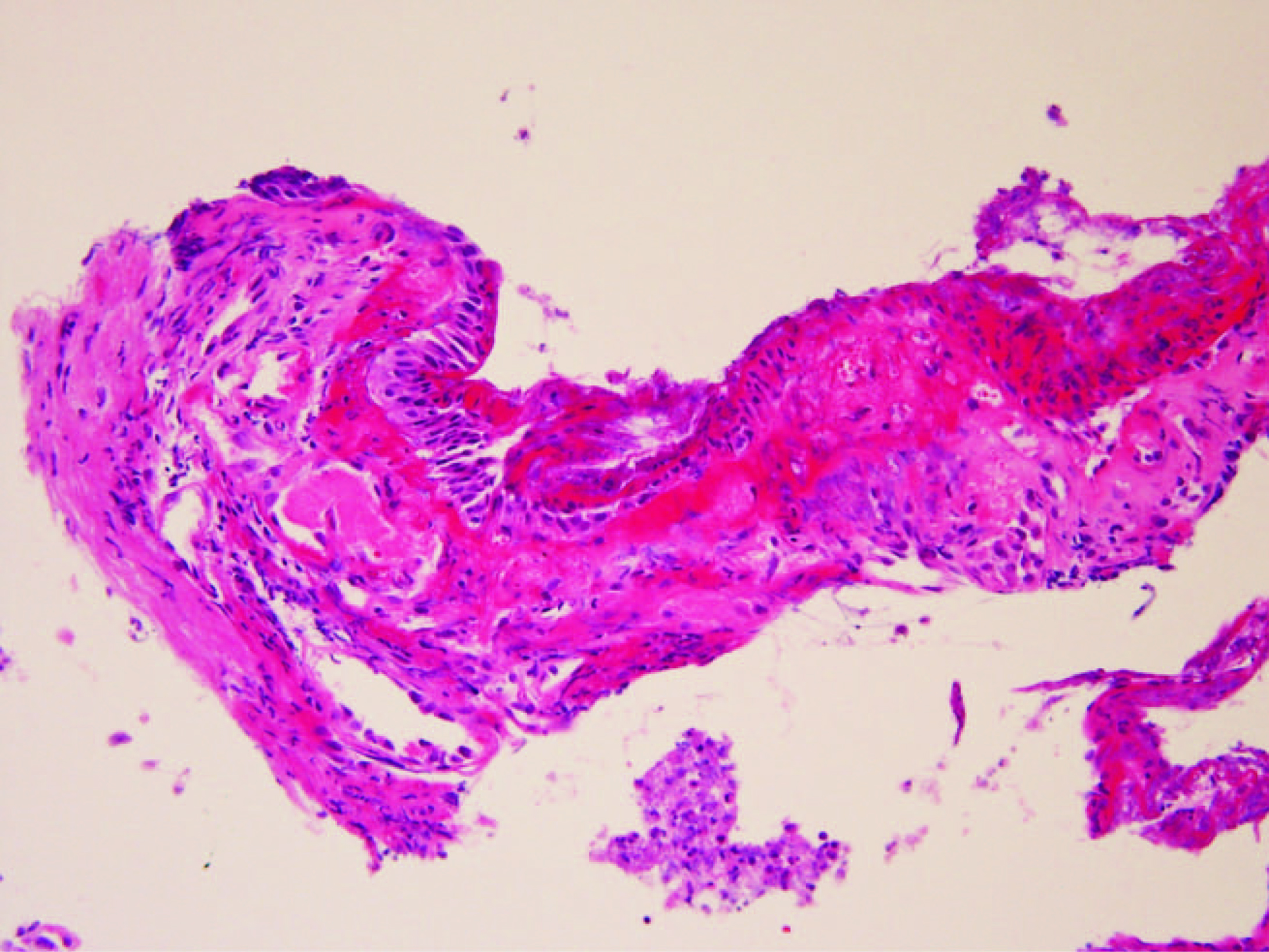
Figure 6. The historogical findings were integrity of the bronchial epithelium, bleeding in the submucosal tissue, neutrophilic and histiocytic infiltration, and changes of suppurative inflammation.
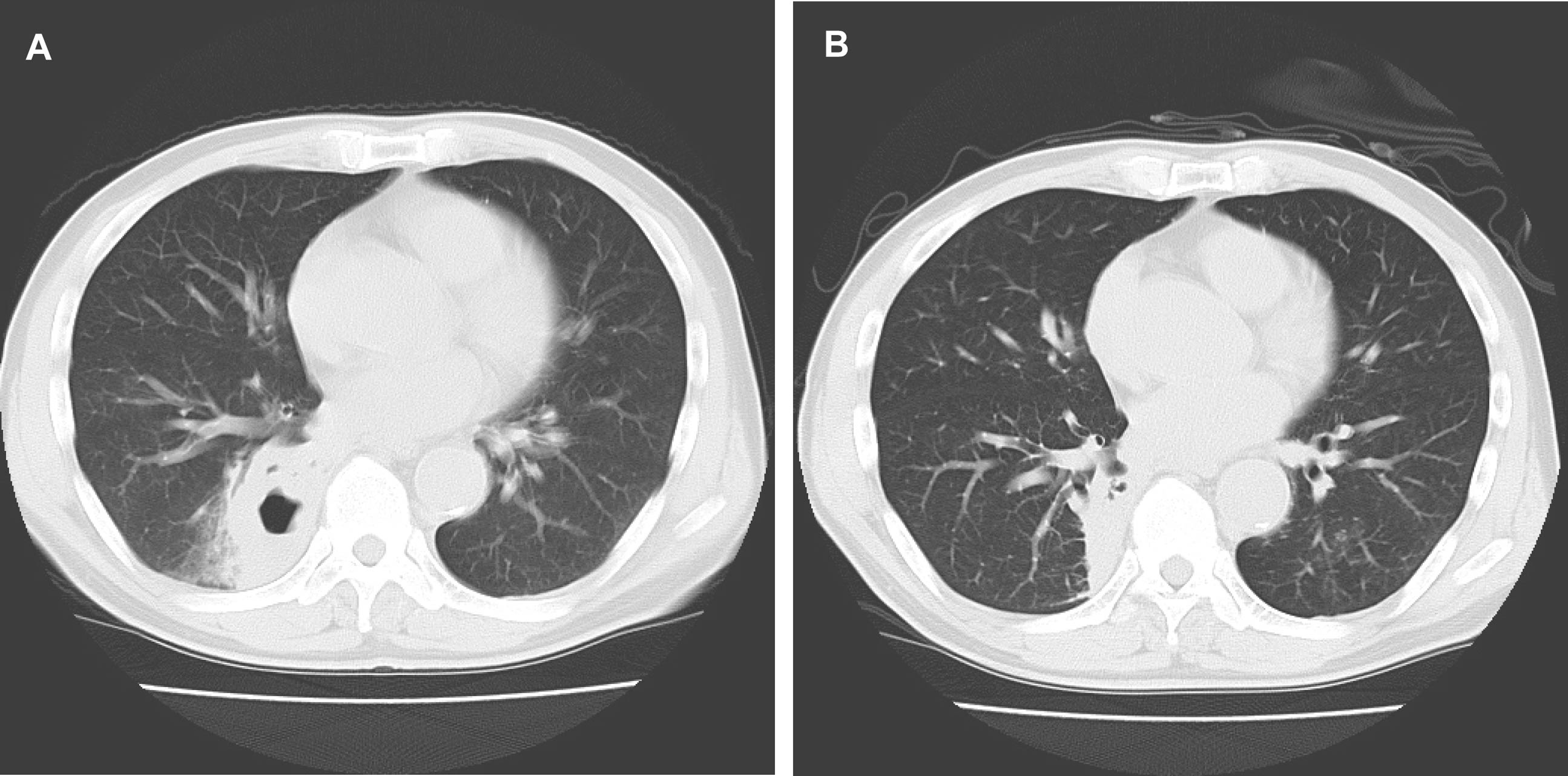
Figure 7. (A) Chest CT showed a lung abscess in right S10; (B) Chest CT showed disappearance of the cavitary lesion.
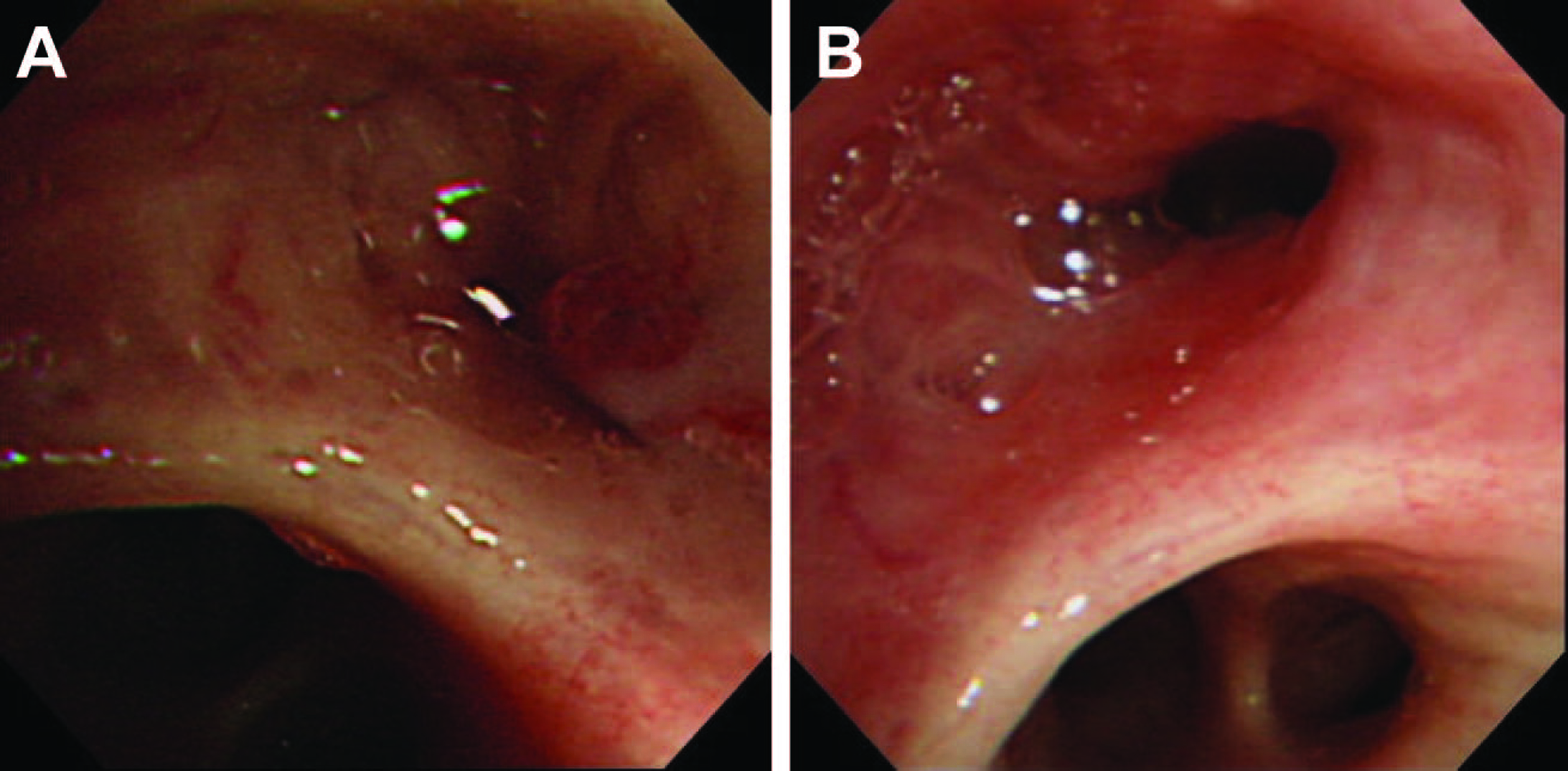
Figure 8. (A) Bronchoscopic findings were a protruding lesion at the opening of right B10, and the lumen was stenosed; (B) A bronchoscopy on day 26 revealed disappearance of the protruding lesion at the opening of right B10, with improvement of the stenosis.
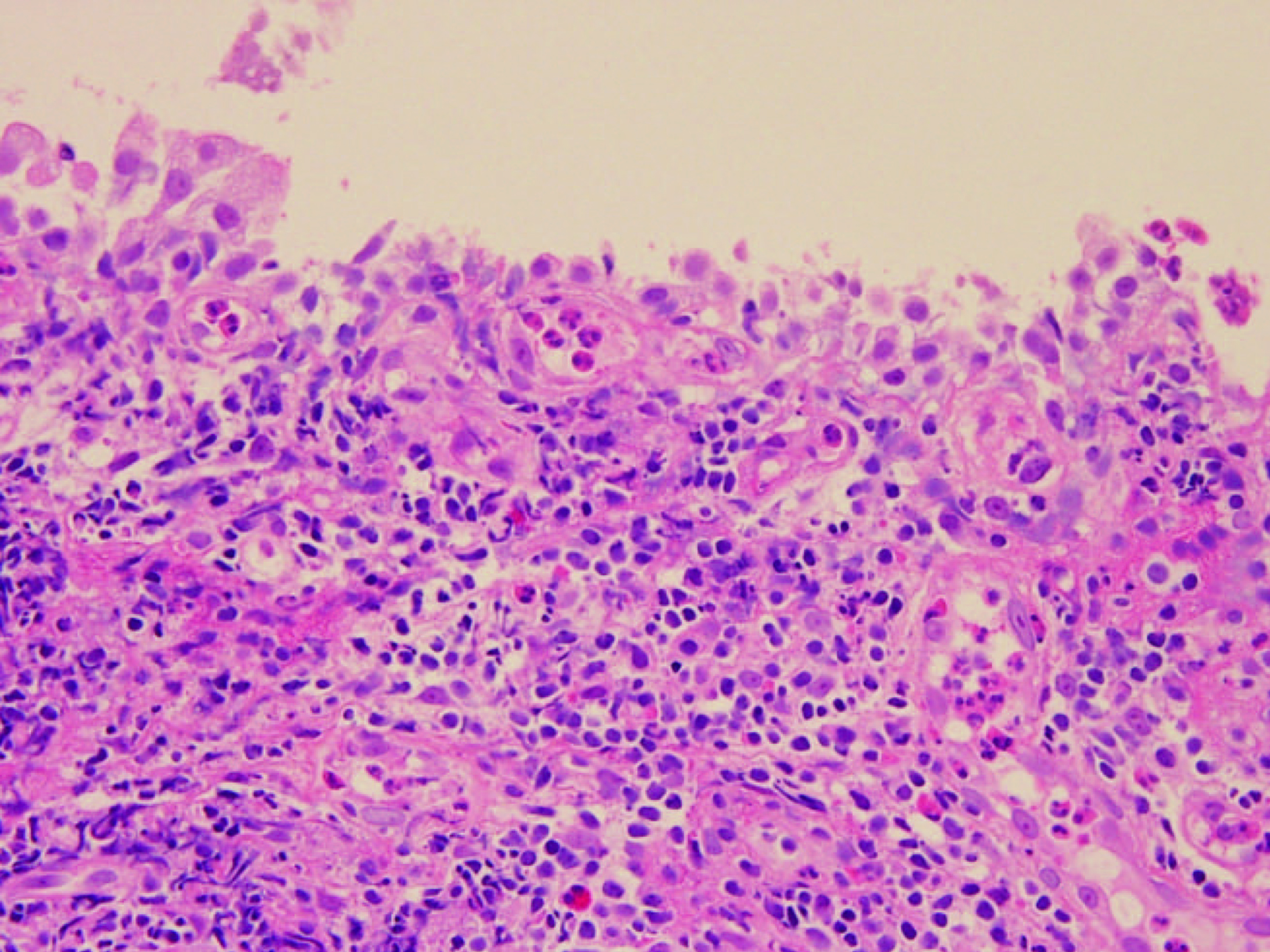
Figure 9. The historogical findings were integrity of the bronchial epithelium and extensive chronic inflammatory cell infiltration, including neutrophils, in the submucosal tissue.









