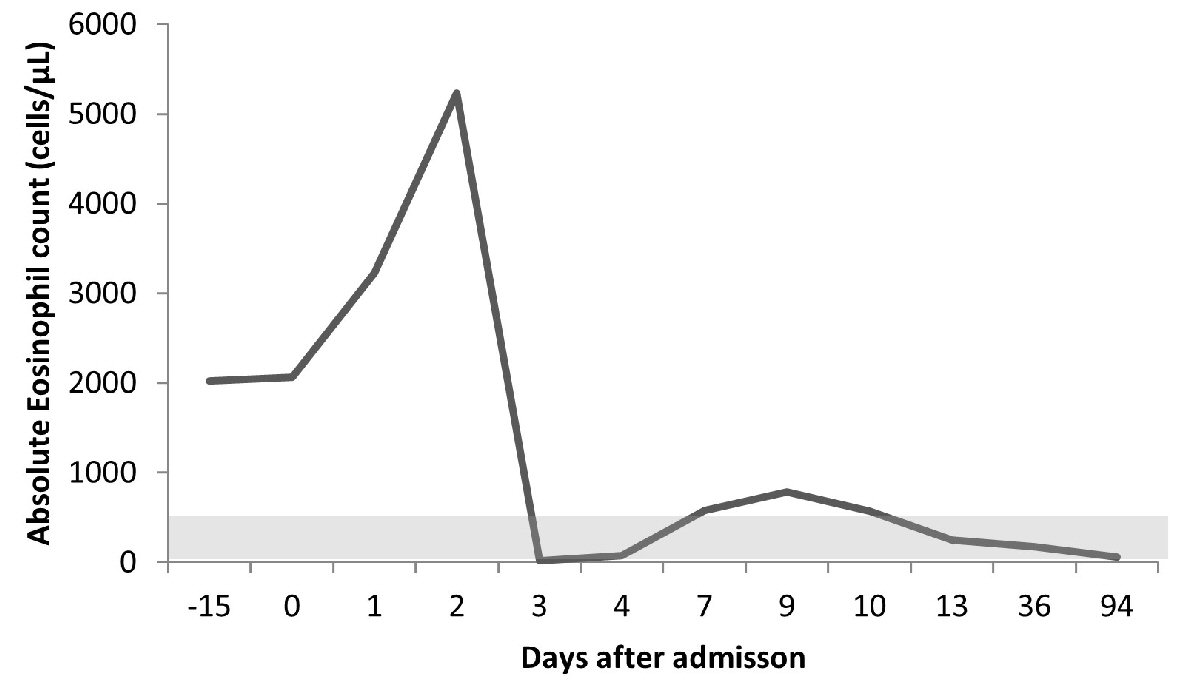
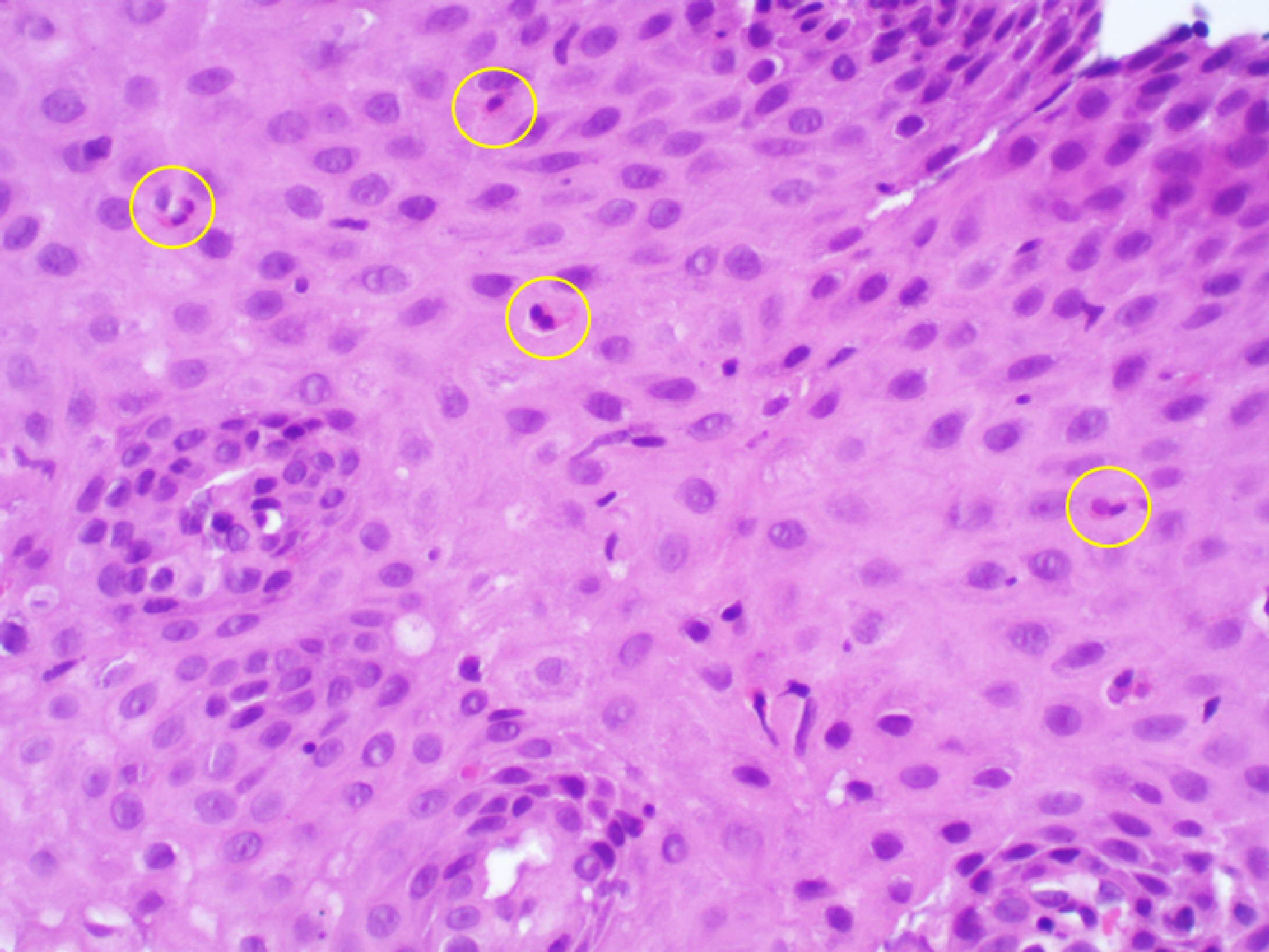
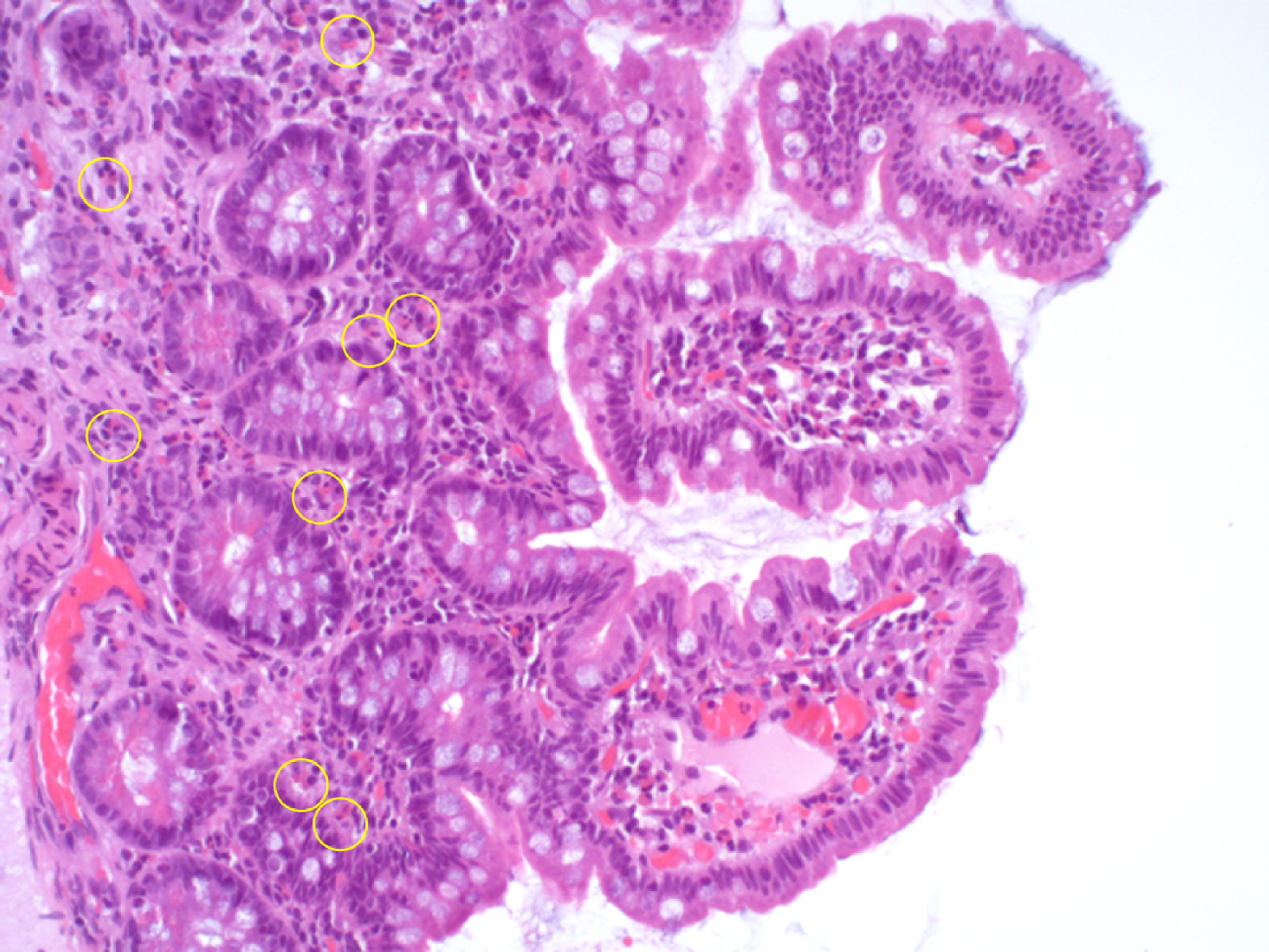
| Immunoglobulins (Igs) | | |
| IgA, mg/dL | 150.0 | 114.0 - 457.0 |
| IgG, mg/dL | 1,061.0 | 793.0 - 1,590.0 |
| IgG1, mg/dL | 778.0 | 240 - 1,118 |
| IgG2, mg/dL | 267.0 | 124 - 549 |
| IgG3, mg/dL | 44.2 | 21 - 134 |
| IgG4, mg/dL | 183.0 | 7 - 89 |
| IgM, mg/dL | 30.9 | 29.0 - 226.0 |
| IgE, KU/L | 13 | < 100 |
| Ig light-chains kappa, mg/dL | 247 | |
| Ig light-chains lambda, mg/dL | 144 | |
| Ratio kappa/lambda | 1.72 | 1.35 - 2.70 |
| Complement (C) | | |
| C3, mg/dL | 119.5 | 81.0 - 167.0 |
| C4, mg/dL | 12.0 | 11.0 - 42.0 |
| Allergy | | |
| Phadiatop | Negative | |
| Tryptase, µg/L | 2.41 | < 11.4 |
| Auto-antibodies (Ab) | | |
| Anti-nuclear antibodies (ANAs) | Negative | |
| Anti-dsDNA, UI/mL | 0.6 | < 15.0 |
| Anti-Sm, U/mL | 0.2 | < 10.0 |
| Anti-SS-A, U/mL | 0.2 | < 10 |
| Anti-SS-B, U/mL | 0.1 | < 10 |
| IgA anti-transglutaminase, U/mL | 0.3 | < 10 |
| Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCAs) | Negative | < 1/20 |
| Anti-proteinase 3 (PR3), UQ | < 2.3 | < 20 |
| Anti-myeloperoxidase (MPO), UQ | 4.1 | < 20 |
| IgA anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibody (ASCA), U/mL | 1.7 | < 10 |
| IgG anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibody (ASCA), U/mL | 0.4 | <10 |
| Serology | | |
| Anti-Treponema pallidum Ab | Negative | |
| Anti-HAV Ab | Negative | |
| Antigen HBs | Negative | |
| Anti-HBs Ab, UI/L | Positive (94.1) | |
| Anti-HBc Ab | Negative | |
| Anti-HCV Ab | Negative | |
| Anti-HIV Ab | Negative | |
| Anti-HTLV I | Negative | |
| Anti-HTLV I | Negative | |
| Fasciola hepatica | < 1/160 | Negative: < 1/160 |
| Toxocara canis | Negative | |
| Schistosoma | Negative | |
| Echinococcus IgG index | 0.7 | Negative: < 9 |
| Strongyloides stercoralis Ab | Negative | |
| Ascaris, kUA/L | 0.01 | < 0.35 |