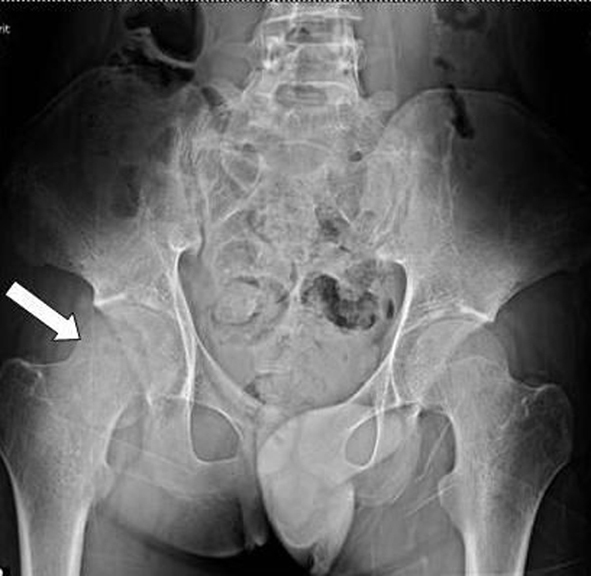
Figure 1. Pelvic radiograph: right femoral head fracture.
| Journal of Medical Cases, ISSN 1923-4155 print, 1923-4163 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Med Cases and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.journalmc.org |
Case Report
Volume 5, Number 7, July 2014, pages 404-407
Lumbosacral Plexopathies: Causing by Femoral Head Fracture
Figures

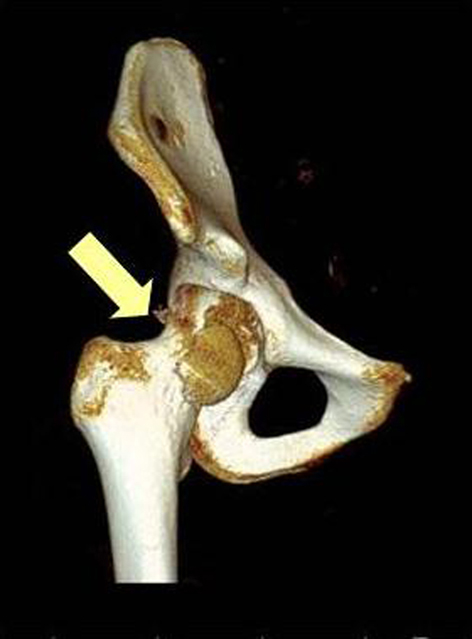
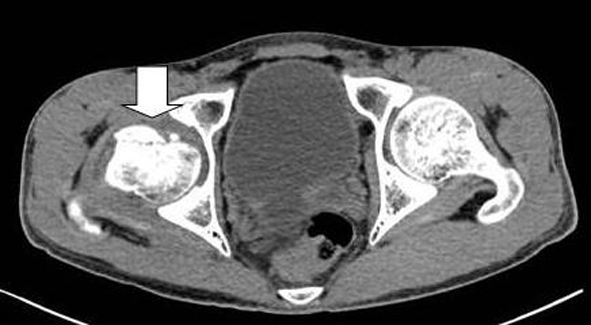
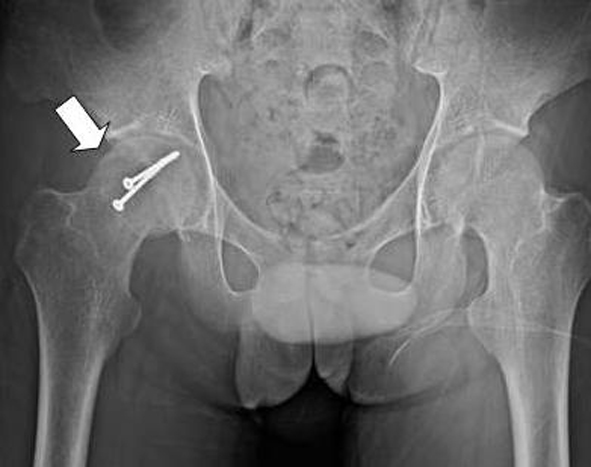
Tables
| Nerve | Latency (ms) | Amplitude (mV) | Velocity (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NR: no electrical response. | |||
| Right sensory superficial peroneal nerve | NR | NR | NR |
| Right motor peroneal nerve | NR | NR | NR |
| Muscle | Insertional activity | Spontaneous activity | Amplitude (mV) | Recruitment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fibrillation | Positive sharp wave | ||||
| Rt. Biceps femoris (long head) | Increased | 2+ | 3+ | 1-3 | Discrete |
| Rt. Biceps femoris (short head) | Increased | 3+ | 3+ | None | None |
| Rt. Gastrocnemius | Increased | 2+ | 4+ | None | None |
| Rt. Gluteus maximus | Increased | 1+ | 2+ | 1 - 2 | Discrete |
| Rt. Tensor fascia latae | Increased | 2+ | 3+ | 0.4 - 1 | Discrete |
| Rt. Tibialis anterior | Increased | 1+ | 3+ | None | None |
| Rt. Rectus femoris | Normal | None | None | 0.5 - 2 | Full |
| Rt. Paravertebral (L5 level) | Normal | None | None | - | - |