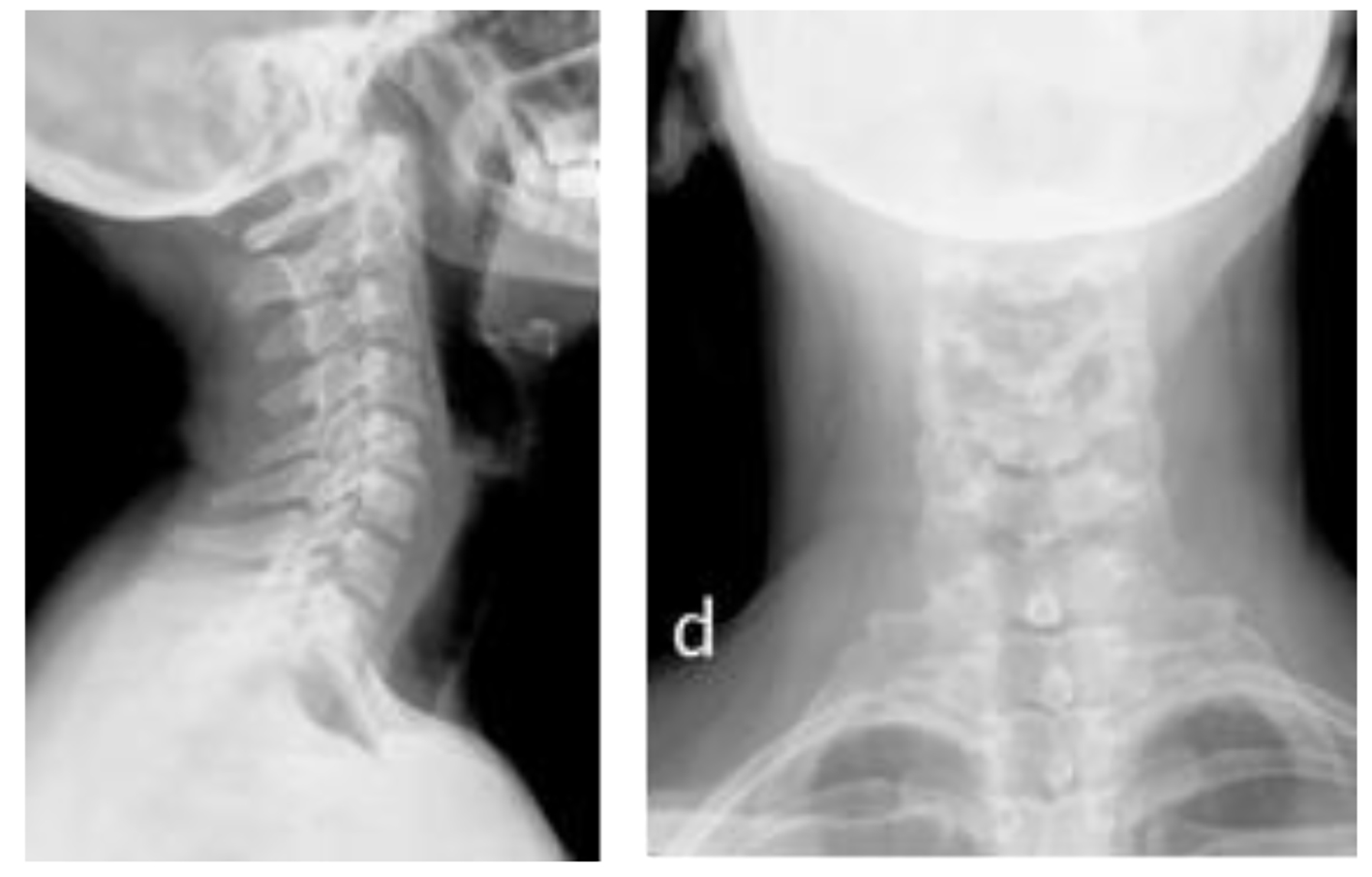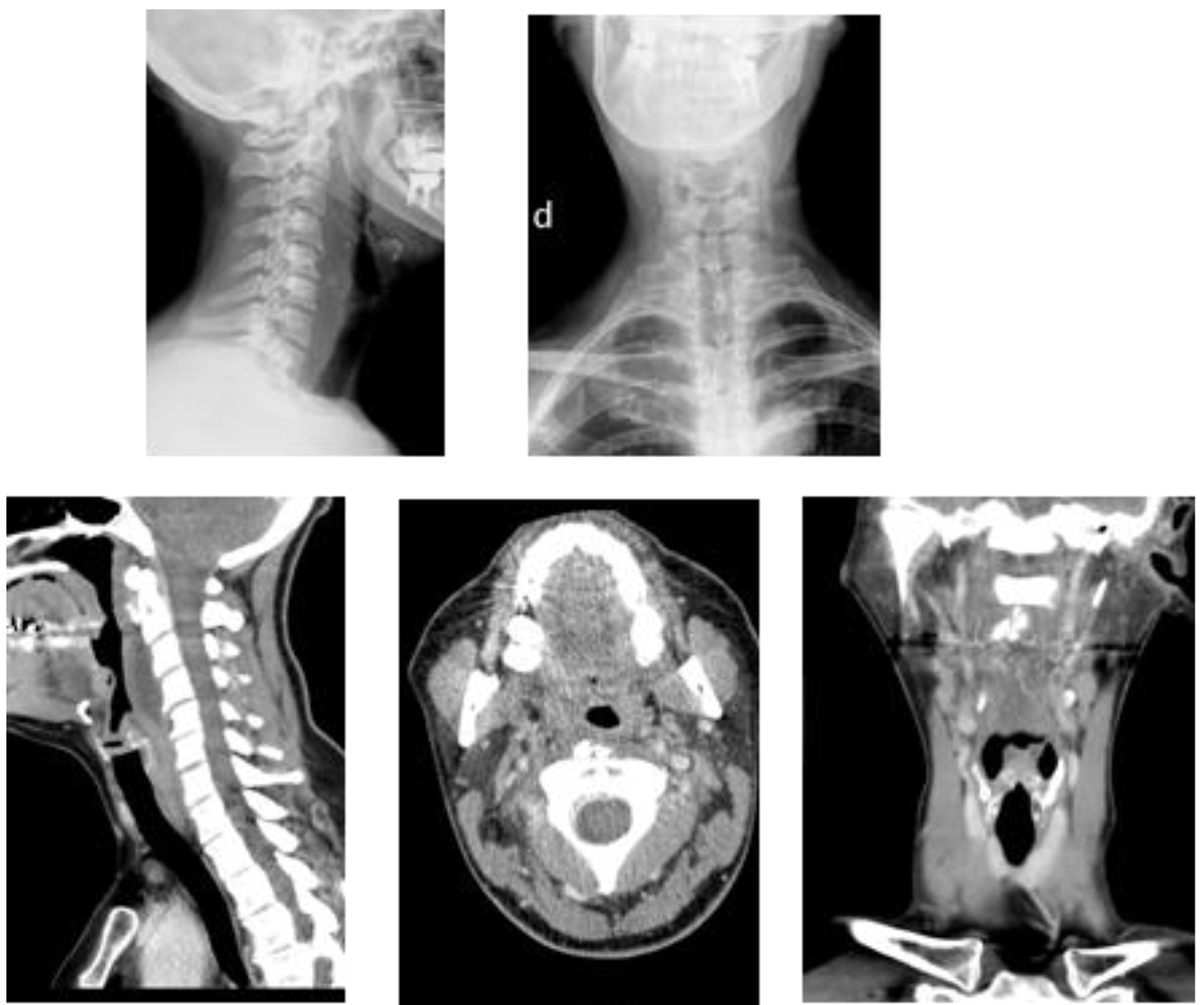
Figure 1. Two images of cervical plain on top. The first side showing rectification of physiological lordosis next to the prevertebral calcifications at level C1-C2 and edematization of the prevertebral space. Pictures of CT on the bottom showing moderate increase of prevertebral soft tissues at the height of C2, C3 and C4 and a tenuous calcification of irregular morphology, approximately 15 × 14.5 × 9.5 mm in intimate relation with the proximal portion of the longus colli muscle belly.