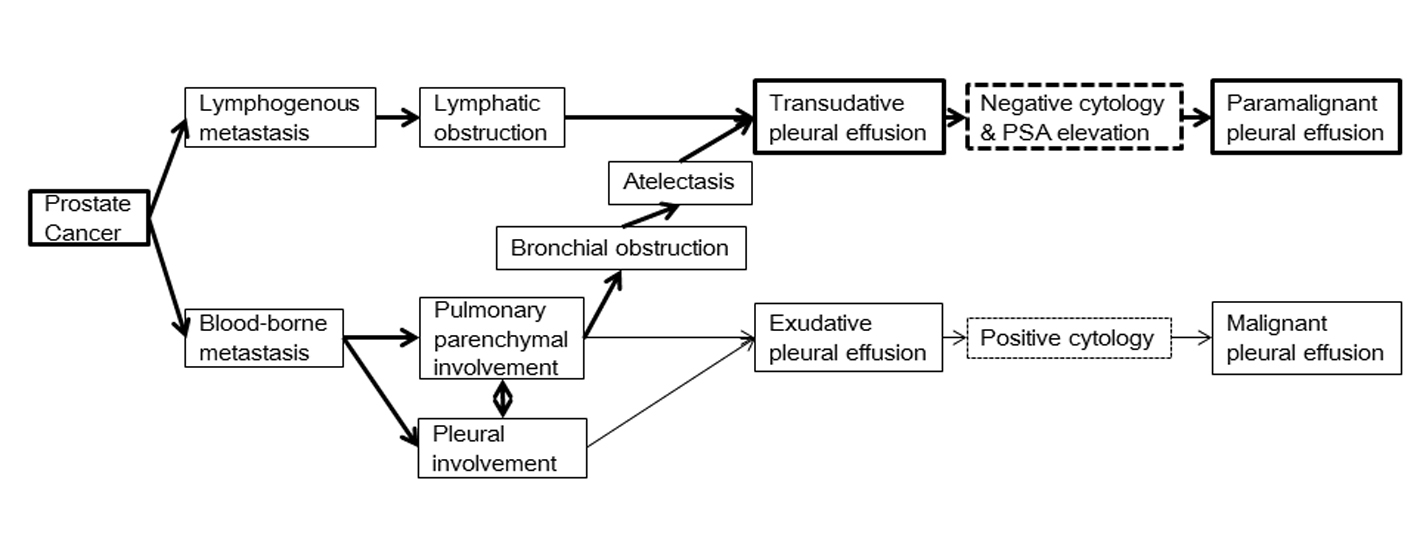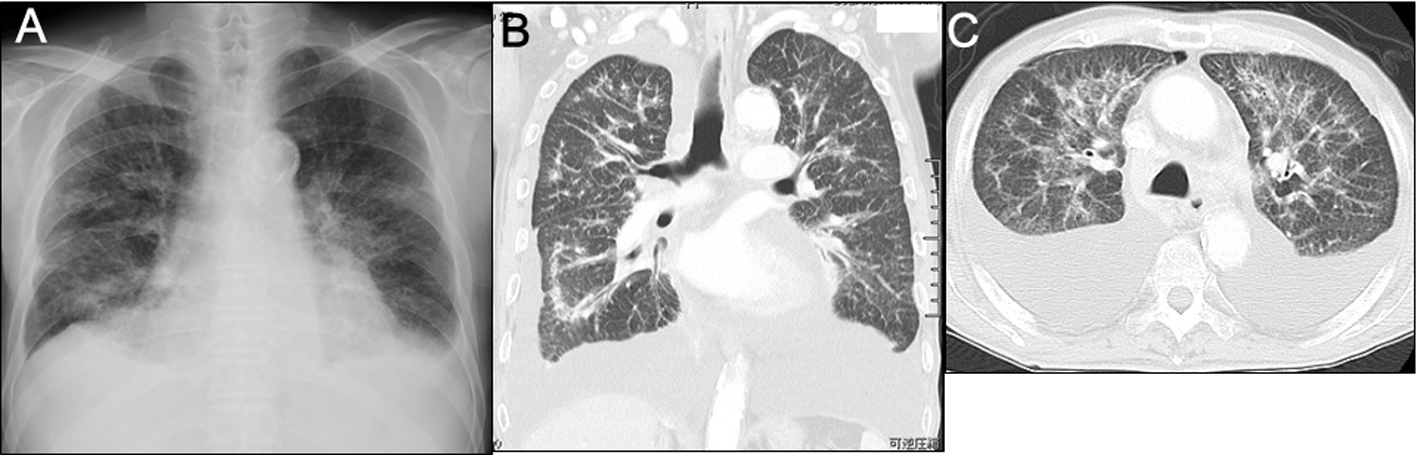
Figure 1. Imaging studies on admission. A) Plain chest radiography showed the cardiothoracic ratio was 55%, bilateral costophrenic angles were dull, and diffuse bilateral reticulonodular opacification was present. B, C) Plain chest computed tomography showed bilateral large amounts of pleural fluid, slight pericardial effusion, patchy consolidation sparing the subpleural regions, and thickenings of both the interlobular septum and pleura.