| Journal of Medical Cases, ISSN 1923-4155 print, 1923-4163 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, J Med Cases and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.journalmc.org |
Case Report
Volume 5, Number 1, January 2014, pages 40-42
Bilateral Chylothorax. An Unusual Presentation in the Course of Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome, HIV Infection and Kaposi’s Sarcoma: A Case Report
Evaggelos Boultadakisa, Maria Chountib, Panagiotis Hountisa, c, Georgios Sotiropoulosa, John Dimitrogloua, Sotirios Moraitisa
aDepartment of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Athens Naval and Veterans Hospital, Deinokratous 70, 11521 Athens, Greece
bNursing School, Technological Institute of Patra, Megalou Alexandrou 1, Koukouli, 26334 Patra, Greece
cCorresponding author: Panagiotis Hountis, Veikou 9-11, 11146 Galatsi, Athens, Greece
Manuscript accepted for publication December 9, 2013
Short title: Bilateral Chylothorax in IRIS Syndrome
doi: https://doi.org/10.4021/jmc1630w
| Abstract | ▴Top |
Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) is a term used to describe the paradoxical worsening of a pre-existing infection or the presentation of a previously undiagnosed condition in HIV-infected patients soon after commencement of antiretroviral therapy (ART). We report a case of a patient with HIV infection and Kaposi sarcoma, who developed bilateral chylothorax as a manifestation of IRIS, after the initiation of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Bilateral chylothorax is extremely rare and has been associated with significant morbidity and mortality. We present here the successful management with bilateral video-assisted thoracic surgery.
Keywords: Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome; Kaposi sarcoma; HIV infection; Chylothorax
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) is a term used to describe the paradoxical worsening of a pre-existing infection or the presentation of a previously undiagnosed condition in HIV-infected patients soon after commencement of antiretroviral therapy (ART) [1]. Contemporary ART is both potent and tolerable for long periods. ART in HIV/AIDS patients leads to dramatic reduction in plasma viral load, improvement in CD4+ T cell counts and partial restoration of overall immune function [2]. It is unclear whether complete immune reconstitution ever occurs, but it is clear that patients who commence ART when they are very immunodeficient are susceptible to immune reconstitution disorders [3].
Disseminated Kaposi’s sarcoma (KS) is a common problem in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Intrathoracic involvement occurs clinically in as many as a fifth of patients with KS [4, 5], and has been reported in 11 of 23 consecutive patients in an autopsy series [6]. Pulmonary KS, usually, follows the appearance of characteristic lesion of the skin [7]. Its clinical and radiographic presentation may mimic pneumonia due to opportunistic infections, although nodular infiltrates and intrathoracic lymph node enlargement are commonly seen. Because pleural effusion only rarely occurs in patients with opportunistic infections, such as Peunonocystis carinii, the presence of pleural effusion in a patient with cutaneous KS suggests the diagnosis of pulmonary KS [8].
Chylous pleural effusion, on the other hand, has been reported previously in only a few patients with KS [9, 10]. Chylothorax represents chyle in the pleural cavity. The presence of chylomicrons and a triglyceride level > 110 mg/dL in the aspirated pleural fluid confirms the diagnosis of chylothorax [11]. We report a case of a patient with HIV and KS, who developed bilateral chylothorax as a manifestation of IRIS, after the initiation of highly active antiretroviral therapy.
| Case Report | ▴Top |
A 37-year-old HIV-infected man was transferred to the thoracic surgery department due to bilateral chylothorax. The patient presented with respiratory distress and also malnutrition, hypovolemia and electrolyte imbalance. During his 30-day hospitalization, a central line and parenteral nutrition with medium chain triglycerides had been started in order to medically treat the condition. The diagnosis of chylothorax was documented based on bilateral thoracentecis with pleurocath and the appearance of a milky (chylous) pleural effusion with an elevated triglyceride level (> 110 mg/dL). One week after pleurocath insertion, a fever up to 38 °C complicated chylothorac. Antibiotis was started (teicoplanin 400 × 2, meropenem 1 × 3, itraconazole sir 10 × 2) along with antiretroviral treatment. The patient was treated with video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) with clip ligation of the thoracic duct with talc pleurodesis at first at the right side (Fig. 1). Twenty days later, we operated on the left side. Postoperatively, in the second operation, the patient developed an acute respiratory distress syndrome and stayed for 24 h at the intensive care unit. The distress syndrome was probably a result of pulmonary edema due to lung re-expansion. Another possible explanation was an systemic reaction due to talc pleurodesis. The patient was extubated 20 h later and was discharged 10 days later in stable clinical condition. Three years later, the patient is stable in excellent clinical condition.
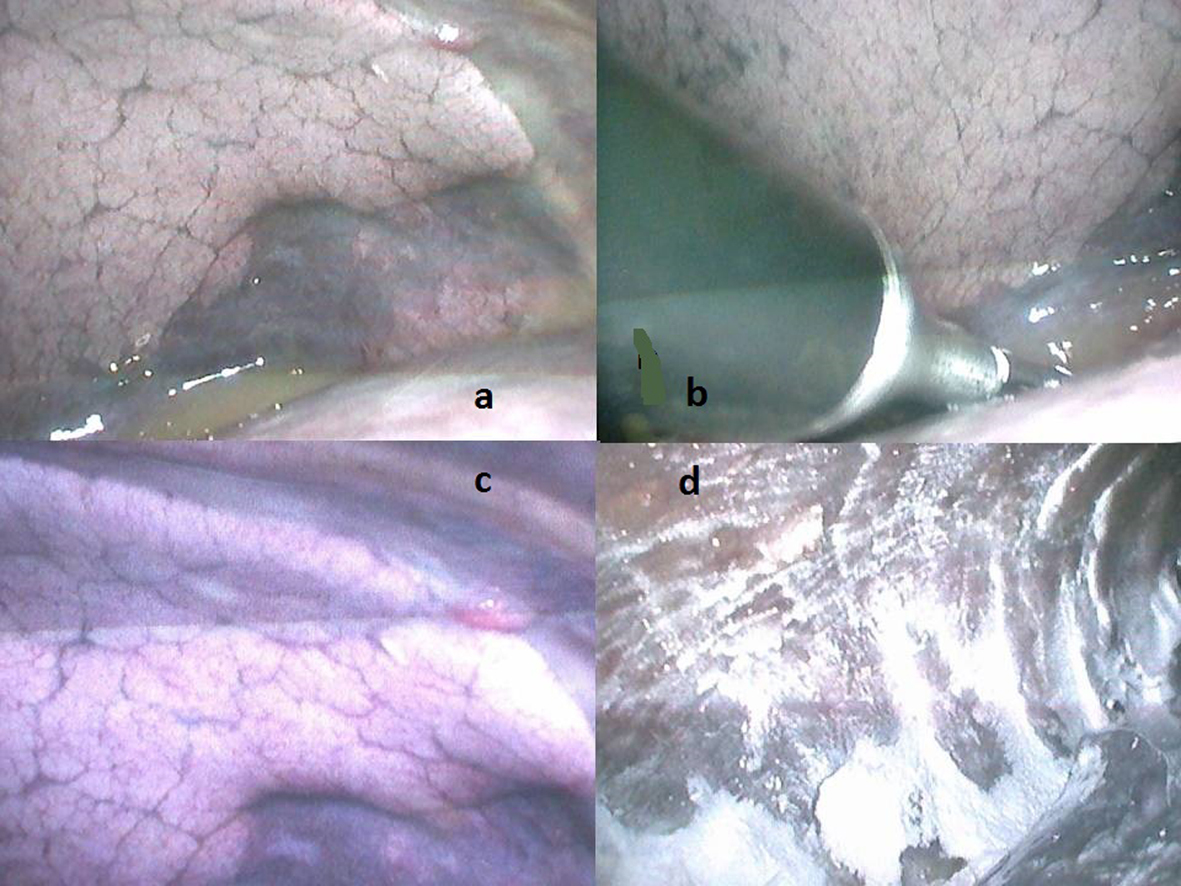 Click for large image | Figure 1. (a) Initial intraoperative view. (b) Thoracoscopic clip ligation of the thoracic duct. (c) Cherry-like appearance of Kaposi’s sarcoma (right upper corner). (d) Final view after talc insufflation, before lung re-expansion. |
| Discussion | ▴Top |
Chylothorax is caused by disruption or obstruction of the thoracic duct. An acute onset of pleural effusion and the presence of turbid fluid that does not clear when centrifuged or that contains at least 1.24 mmol/L (110 mg/dL) triglyceride establish the diagnosis [12]. In advanced HIV infection, chylothorax may also be caused by infiltration of the thoracic duct by KS [13].
Chylothorax, the presence of lymph in the pleural space, has remained a difficult clinical challenge for which the ideal treatment has not been well established. The general approach to the problem varies in that some clinicians adopt early surgical intervention while others adopt a conservative approach to the problem.
The treatment of chylous pleural effusions required prompt and aggressive measures. Although conservative approach may have a role to play in small chylothoraces, therapeutic thoracentesis and tube thoracostomy are the initial step in large chylothoraces that cause respiratory distress. During the period of excessive chyle leak, patients are generally advised nil by mouth or a diet rich in low fat, medium-chain triglycerides. Many follow guidelines that Selle and associates [14] suggested. They propose surgery in trauma, daily loss of chyle exceeds 1,500 mL in adults or > 100 mL/kg body weight per day in a child, when the output of chyle is not diminished over a 14-day period, or when nutritional complications seem imminent [15]. Graham et al recommend that surgical intervention is highly effective and seems warranted if the chylothorax has not responded after 5-7 day trial of medical therapy in both adults and children [16].
Our patient was treated with VATS with talc pleurodesis and the result was excellent. Its use specially for chylothorax has only a few case reports [17].
VATS offers the advantage of access to the entire hemithorax with excellent visualization of the mediastinal structures including the thoracic duct, without the morbidity of thoracotomy. It also allows application of clips to the thoracic duct at the aortic hiatus, or to thoracic duct injuries or pleural defects at other sites. Finally, it allows chemical pleurodesis and application of talc or fibrin glue as required.
In the past, the mortality due to chylothorax was in excess of 50%. Currently, the morbidity and mortality have improved due to the more aggressive management strategies adopted. VATS offers the advantage of successful treatment of chylothorax while avoiding thoracotomy. The limited incisions of thoracoscopy produce less postoperative pain, less rehabilitation time and less recovery time, while accomplishing the same desired outcome. We strongly propose VATS for the management of chylothorax for these reasons.
Conflict of Interest
None.
| References | ▴Top |
- French MA. HIV/AIDS: immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome: a reappraisal. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;48(1):101-107.
doi pubmed - Sharma SK, Soneja M. HIV & immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS). Indian J Med Res. 2011;134(6):866-877.
doi pubmed - French MA. Disorders of immune reconstitution in patients with HIV infection responding to antiretroviral therapy. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2007;4(1):16-21.
doi pubmed - Ognibene FP, Steis RG, Macher AM, Liotta L, Gelmann E, Pass HI, Lane HC,
et al . Kaposi's sarcoma causing pulmonary infiltrates and respiratory failure in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1985;102(4):471-475.
doi pubmed - Garay SM, Belenko M, Fazzini E, Schinella R. Pulmonary manifestations of Kaposi's sarcoma. Chest. 1987;91(1):39-43.
doi - Meduri GU, Stover DE, Lee M, Myskowski PL, Caravelli JF, Zaman MB. Pulmonary Kaposi's sarcoma in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Clinical, radiographic, and pathologic manifestations. Am J Med. 1986;81(1):11-18.
doi - Pennington DW, Warnock ML, Stulbarg MS. Chylothorax and respiratory failure in Kaposi's sarcoma. West J Med. 1990;152(4):421-422.
pubmed - Zibrak JD, Silvestri RC, Costello P, Marlink R, Jensen WA, Robins A, Rose RM. Bronchoscopic and radiologic features of Kaposi's sarcoma involving the respiratory system. Chest. 1986;90(4):476-479.
doi pubmed - Schulman LL, Grimes MM. Metastatic Kaposi's sarcoma and bilateral chylothorax. N Y State J Med. 1986;86(4):205-206.
pubmed - Pandya K, Lal C, Tuchschmidt J, Boylen CT, Sharma OP. Bilateral chylothorax with pulmonary Kaposi's sarcoma. Chest. 1988;94(6):1316-1317.
doi pubmed - Nair SK, Petko M, Hayward MP. Aetiology and management of chylothorax in adults. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2007;32(2):362-369.
doi pubmed - Staats BA, Ellefson RD, Budahn LL, Dines DE, Prakash UB, Offord K. The lipoprotein profile of chylous and nonchylous pleural effusions. Mayo Clin Proc. 1980;55(11):700-704.
pubmed - Marais BJ, Pienaar J, Gie RP. Kaposi sarcoma with upper airway obstruction and bilateral chylothoraces. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003;22(10):926-928.
doi pubmed - Selle JG, Snyder WH
3rd , Schreiber JT. Chylothorax: indications for surgery. Ann Surg. 1973;177(2):245-249.
doi pubmed - Marts BC, Naunheim KS, Fiore AC, Pennington DG. Conservative versus surgical management of chylothorax. Am J Surg. 1992;164(5):532-534, discussion 534-535.
doi - Rheuban KS, Kron IL, Carpenter MA, Gutgesell HP, Rodgers BM. Pleuroperitoneal shunts for refractory chylothorax after operation for congenital heart disease. Ann Thorac Surg. 1992;53(1):85-87.
doi - Kent RB
3rd , Pinson TW. Thoracoscopic ligation of the thoracic duct. Surg Endosc. 1993;7(1):52-53.
doi pubmed
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Medical Cases is published by Elmer Press Inc.








